Identification of developmentally specific enhancers for Tsix in the regulation of X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 15767680
- PMCID: PMC1061649
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.7.2757-2769.2005
Identification of developmentally specific enhancers for Tsix in the regulation of X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
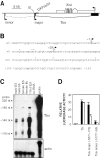
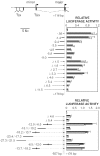
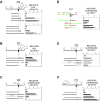
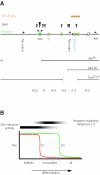
X chromosome inactivation silences one of two X chromosomes in the mammalian female cell and is controlled by a binary switch that involves interactions between Xist and Tsix, a sense-antisense pair of noncoding genes. On the future active X chromosome, Tsix expression suppresses Xist upregulation, while on the future inactive X chromosome, Tsix repression is required for Xist-mediated chromosome silencing. Thus, understanding the binary switch mechanism depends on ascertaining how Tsix expression is regulated. Here we have taken an unbiased approach toward identifying Tsix regulatory elements within the X chromosome inactivation center. First, we defined the major Tsix promoter and found that it cannot fully recapitulate the developmental dynamics of Tsix expression, indicating a requirement for additional regulatory elements. We then delineated two enhancers, one classical enhancer mapping upstream of Tsix and a bipartite enhancer that flanks the major Tsix promoter. These experiments revealed the intergenic transcription element Xite as an enhancer of Tsix and the repeat element DXPas34 as a component of the bipartite enhancer. Each enhancer contains DNase I-hypersensitive sites and appears to confer developmental specificity to Tsix expression. Characterization of these enhancers will facilitate the identification of trans-acting regulatory factors for X chromosome counting and choice.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tsix, a gene antisense to Xist at the X-inactivation centre.Nat Genet. 1999 Apr;21(4):400-4. doi: 10.1038/7734. Nat Genet. 1999. PMID: 10192391
-
A functional role for Tsix transcription in blocking Xist RNA accumulation but not in X-chromosome choice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Aug 28;98(18):10232-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.171243598. Epub 2001 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11481444 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF, a candidate trans-acting factor for X-inactivation choice.Science. 2002 Jan 11;295(5553):345-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1065982. Epub 2001 Dec 6. Science. 2002. PMID: 11743158
-
X-tra! X-tra! News from the mouse X chromosome.Dev Biol. 2006 Oct 15;298(2):344-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.07.011. Epub 2006 Jul 15. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16916508 Review.
-
An embryonic story: analysis of the gene regulative network controlling Xist expression in mouse embryonic stem cells.Bioessays. 2010 Jul;32(7):581-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.201000019. Bioessays. 2010. PMID: 20544740 Review.
Cited by
-
Cis- and trans-regulation in X inactivation.Chromosoma. 2016 Mar;125(1):41-50. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0525-x. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26198462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Intersection of Tsix and Hedgehog Signaling during the Initiation of X-Chromosome Inactivation.Dev Cell. 2017 Nov 6;43(3):359-371.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.09.027. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 29107559 Free PMC article.
-
A boundary element between Tsix and Xist binds the chromatin insulator Ctcf and contributes to initiation of X-chromosome inactivation.Genetics. 2011 Oct;189(2):441-54. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.132662. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21840866 Free PMC article.
-
The X as model for RNA's niche in epigenomic regulation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Sep;2(9):a003749. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003749. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20739414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping of DNA replication origins to noncoding genes of the X-inactivation center.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 May;26(10):3707-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.10.3707-3717.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16648467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., et al. (ed.). 1995. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Avner, P., and E. Heard. 2001. X-chromosome inactivation: counting, choice and initiation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2:59-67. - PubMed
-
- Avner, P., M. Prissette, D. Arnaud, B. Courtier, C. Cecchi, and E. Heard. 1998. Molecular correlates of the murine Xce locus. Genet. Res. 72:217-224. - PubMed
-
- Bell, A. C., and G. Felsenfeld. 2000. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature 405:482-485. - PubMed
-
- Bell, A. C., A. G. West, and G. Felsenfeld. 1999. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell 98:387-396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
