Risk of cardiac death after adjuvant radiotherapy for breast cancer
- PMID: 15770005
- PMCID: PMC1853253
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/dji067
Risk of cardiac death after adjuvant radiotherapy for breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Women with breast cancer who are treated with adjuvant radiation have a decreased risk of local recurrence but an increased risk of mortality from ischemic heart disease. Patients with left-sided breast tumors receive a higher dose of radiation to the heart than patients with right-sided tumors. Because radiation techniques have improved over time, we investigated whether the risk of death from ischemic heart disease after adjuvant breast radiotherapy decreased over time.
Methods: We used the 12-registry 1973-2000 dataset from the National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program. Women (n = 27,283) treated with adjuvant radiation for breast cancer diagnosed in 1973-1989 were included in the study. Ischemic heart disease mortality was calculated at 15 years and compared for women diagnosed during 1973-1979, 1980-1984, and 1985-1989. Cox proportional hazards models were used to calculate the hazard of death from ischemic heart disease for women diagnosed 1973-1988 and censored at 12 years. All statistical tests were two-sided.
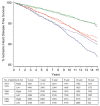
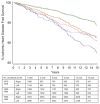
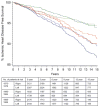
Results: There were no differences in age, race/ethnicity, disease stage, or follow-up time between the 13 998 women with left-sided and 13 285 with right-sided cancer. For women diagnosed in 1973-1979, there was a statistically significant difference in 15-year mortality from ischemic heart disease between patients with left-sided (13.1%, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 11.6 to 14.6) and those with right-sided (10.2%, 95% CI = 8.9 to 11.5) breast cancer (P = .02); no such difference was found for women diagnosed in 1980-1984 (9.4%, [95% CI = 8.1 to 10.6] versus 8.7% [95% CI = 7.4 to 10.0], respectively, P = .64) or 1985-1989 (5.8% [95% CI = 4.8 to 6.8] versus 5.2% [95% CI = 4.4 to 5.9], respectively, P = .98). In the Cox model, the hazard ratio [HR] for ischemic heart disease mortality for women with left-sided versus women with right-sided disease was 1.50 (95% CI = 1.19 to 1.87) in 1979. With each succeeding year after 1979, the hazard of death from ischemic heart disease for women with left-sided versus those with right-sided disease declined by 6% (HR = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.91 to 0.98).
Conclusions: Risk of death from ischemic heart disease associated with radiation for breast cancer has substantially decreased over time.
Figures
Comment in
-
Radiotherapy for breast cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005 Mar 16;97(6):406-7. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dji086. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005. PMID: 15769997 No abstract available.
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. SEER*Stat Database: Incidence-SEER 12 Regs Public-Use, Nov 2002 Sub (1973–2000), National Cancer Institute, DCCPS, Surveillance Research Program, Cancer Statistics Branch, released April 2003, based on the November 2002 submission. [CD-Rom]
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Redmond CK, Wolmark N, Wickerham DL, Cronin WM. Reanalysis and results after 12 years of follow-up in a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy with lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1456–61. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous Favourable and unfavourable effects on long-term survival of radiotherapy for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group [see comment] Lancet. 2000;355:1757–70. - PubMed
-
- Overgaard M, Hansen PS, Overgaard J, Rose C, Andersson M, Bach F, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk premenopausal women with breast cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group 82b. Trial N Engl J Med. 1997;337:949–55. - PubMed
-
- Overgaard M, Jensen MB, Overgaard J, Hansen PS, Rose C, Andersson M, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk postmenopausal breast-cancer patients given adjuvant tamoxifen: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group DBCG 82c randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;353:1641–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

