Engineering and characterisation of chimeric monoclonal antibody 806 (ch806) for targeted immunotherapy of tumours expressing de2-7 EGFR or amplified EGFR
- PMID: 15770208
- PMCID: PMC2361945
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602470
Engineering and characterisation of chimeric monoclonal antibody 806 (ch806) for targeted immunotherapy of tumours expressing de2-7 EGFR or amplified EGFR
Abstract
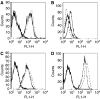
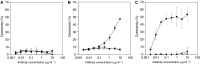
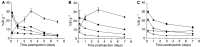
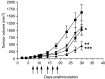
We report the generation of a chimeric monoclonal antibody (ch806) with specificity for an epitope on the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that is different from that targeted by all other anti-EGFR therapies. Ch806 antibody is reactive to both de2-7 and overexpressed wild-type (wt) EGFR but not native EGFR expressed in normal tissues at physiological levels. Ch806 was stably expressed in CHO (DHFR -/-) cells and purified for subsequent characterisation and validated for use in preliminary immunotherapy investigations. Ch806 retained the antigen binding specificity and affinity of the murine parental antibody. Furthermore, ch806 displayed enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against target cells expressing the 806 antigen in the presence of human effector cells. Ch806 was successfully radiolabelled with both iodine-125 and indium-111 without loss of antigen binding affinity or specificity. The radioimmunoconjugates were stable in the presence of human serum at 37 degrees C for up to 9 days and displayed a terminal half-life (T(1/2beta)) of approximately 78 h in nude mice. Biodistribution studies undertaken in BALB/c nude mice bearing de2-7 EGFR-expressing or amplified EGFR-expressing xenografts revealed that (125)I-labelled ch806 failed to display any significant tumour retention. However, specific and prolonged tumour localisation of (111)In-labelled ch806 was demonstrated with uptake of 31%ID g(-1) and a tumour to blood ratio of 5 : 1 observed at 7 days postinjection. In vivo therapy studies with ch806 demonstrated significant antitumour effects on established de2-7 EGFR xenografts in BALB/c nude mice compared to control, and both murine 806 and the anti-EGFR 528 antibodies. These results support a potential therapeutic role of ch806 in the treatment of suitable EGFR-expressing tumours, and warrants further investigation of the potential of ch806 as a therapeutic agent.
Figures

References
-
- Arteaga CL (2002) Overview of epidermal growth factor receptor biology and its role as a therapeutic target in human neoplasia. Semin Oncol 29: 3–9 - PubMed
-
- Bier H, Hoffmann T, Hauser U, Wink M, Ochler M, Kovar A, Muser M, Knecht R (2001) Clinical trial with escalating doses of the antiepidermal growth factor receptor humanized monoclonal antibody EMD 72 000 in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 47: 519–524 - PubMed
-
- Busam KJ, Capodieci P, Motzer R, Kiehn T, Phelan D, Halpern AC (2001) Cutaneous side-effects in cancer patients treated with the antiepidermal growth factor receptor antibody C225. Br J Dermatol 144: 1169–1176 - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159 - PubMed
-
- Clark M (2000) Antibody humanization: a case of the ‘Emperor's new clothes’? Immunol Today 21: 397–402 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

