The many facets of H/ACA ribonucleoproteins
- PMID: 15770508
- PMCID: PMC4313906
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-005-0333-9
The many facets of H/ACA ribonucleoproteins
Abstract
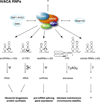
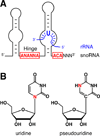
The H/ACA ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) are known as one of the two major classes of small nucleolar RNPs. They predominantly guide the site-directed pseudouridylation of target RNAs, such as ribosomal and spliceosomal small nuclear RNAs. In addition, they process ribosomal RNA and stabilize vertebrate telomerase RNA. Taken together, the function of H/ACA RNPs is essential for ribosome biogenesis, pre-mRNA splicing, and telomere maintenance. Every cell contains 100-200 different species of H/ACA RNPs, each consisting of the same four core proteins and one function-specifying H/ACA RNA. Most of these RNPs reside in nucleoli and Cajal bodies and mediate the isomerization of specific uridines to pseudouridines. Catalysis of the reaction is mediated by the putative pseudouridylase NAP57 (dyskerin, Cbf5p). Unexpectedly, mutations in this housekeeping enzyme are the major determinants of the inherited bone marrow failure syndrome dyskeratosis congenita. This review details the many diverse functions of H/ACA RNPs, some yet to be uncovered, with an emphasis on the role of the RNP proteins. The multiple functions of H/ACA RNPs appear to be reflected in the complex phenotype of dyskeratosis congenita.
Figures


References
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV. Novel predicted RNA-binding domains associated with the translation machinery. J. Mol. Evol. 1999;48:291–302. - PubMed
-
- Arnez JG, Steitz TA. Crystal structure of unmodified tRNA(Gln) complexed with glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase and ATP suggests a possible role for pseudo-uridines in stabilization of RNA structure. Biochemistry. 1994;33:7560–7567. - PubMed
-
- Bachellerie JP, Cavaille J, Huttenhofer A. The expanding snoRNA world. Biochimie. 2002;84:775–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

