How neutrophils kill microbes
- PMID: 15771570
- PMCID: PMC2092448
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115653
How neutrophils kill microbes
Abstract
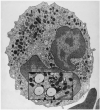
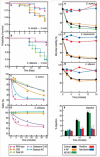
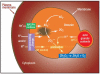
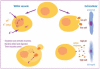
Neutrophils provide the first line of defense of the innate immune system by phagocytosing, killing, and digesting bacteria and fungi. Killing was previously believed to be accomplished by oxygen free radicals and other reactive oxygen species generated by the NADPH oxidase, and by oxidized halides produced by myeloperoxidase. We now know this is incorrect. The oxidase pumps electrons into the phagocytic vacuole, thereby inducing a charge across the membrane that must be compensated. The movement of compensating ions produces conditions in the vacuole conducive to microbial killing and digestion by enzymes released into the vacuole from the cytoplasmic granules.
Figures

References
-
- Iyer GYN, Islam DMF, Quastel JH. Biochemical aspects of phagocytosis. Nature. 1961;192:535–41.
-
- Klebanoff SJ, White LR. Iodination defect in the leukocytes of a patient with chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. N. Engl. J. Med. 1969;280:460–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

