Regulation of YKL-40 expression during genotoxic or microenvironmental stress in human glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 15771622
- PMCID: PMC11158589
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00026.x
Regulation of YKL-40 expression during genotoxic or microenvironmental stress in human glioblastoma cells
Abstract
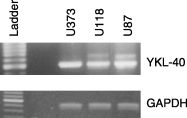
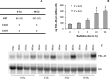
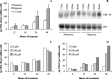
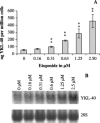
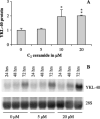
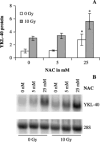
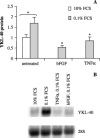
YKL-40 is a 40 kDa secreted glycoprotein belonging to the family of 'mammalian chitinase-like proteins', but without chitinase activity. YKL-40 has a proliferative effect on fibroblasts, chondrocytes and synoviocytes, and chemotactic effect on endothelium and vascular smooth muscle cells. Elevated YKL-40 levels are found in serum of patients with diseases characterized by inflammation, fibrosis and tissue remodeling. Several studies have reported that high serum YKL-40 levels in patients with cancer are associated with poor prognosis. YKL-40 expression is strongly elevated in serum and biopsy material from glioblastomas patients. We investigated the expression of YKL-40 in three human malignant glioma cell lines exposed to different types of stress. Whereas a polymerase chain reaction transcript was detectable in all three cell lines, only U87 produced measurable amounts of YKL-40 protein. In U87, hypoxia and ionizing radiation induced a significant increase in YKL-40 after 24-48 h. The hypoxic induction of YKL-40 was independent of HIF1. Etoposide, ceramide, serum depletion and confluence all led to elevated YKL-40. Inhibition of p53 augmented the YKL-40 expression indicating that YKL-40 is attenuated by p53. In contrast, both basic fibroblast growth factor and tumor necrosing factor-alpha repressed YKL-40. These are the first data on regulation of YKL-40 in cancer cells. Diverse types of stress resulted in YKL-40 elevation, which strongly supports an involvement of YKL-40 in the malignant phenotype as a cellular survival factor in an adverse microenvironment.
Figures

References
-
- Johansen JS, Williamson MK, Rice JS, Price PA. Identification of proteins secreted by human osteoblastic cells in culture. J Bone Miner Res 1992; 7: 501–12. - PubMed
-
- Hakala BE, White C, Recklies AD. Human cartilage gp‐39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 25803–10. - PubMed
-
- Millis AJ, Hoyle M, Reich E, Mann DM. Isolation and characterization of a Mr = 38,000 protein from differentiating smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 1985; 260: 3754–61. - PubMed
-
- Shackelton LM, Mann DM, Millis AJ. Identification of a 38‐kDa heparin‐binding glycoprotein (gp38k) in differentiating vascular smooth muscle cells as a member of a group of proteins associated with tissue remodeling. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 13076–83. - PubMed
-
- Malinda KM, Ponce L, Kleinman HK, Shackelton LM, Millis AJ. Gp38k, a protein synthesized by vascular smooth muscle cells, stimulates directional migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 1999; 250: 168–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

