Efficacy of acupuncture for cocaine dependence: a systematic review & meta-analysis
- PMID: 15771785
- PMCID: PMC1079914
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7517-2-4
Efficacy of acupuncture for cocaine dependence: a systematic review & meta-analysis
Abstract
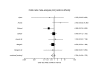
: BACKGROUND: Acupuncture is a commonly used treatment option for the treatment of addictions such as alcohol, nicotine and drug dependence. We systematically reviewed and meta-analyzed the randomized controlled trials of acupuncture for the treatment of cocaine addiction. METHODS: Two reviewers independently searched 10 databases. Unpublished studies were sought using Clinicaltrials.gov, the UK National Research Register and contacting content experts. Eligible studies enrolled patients with the diagnosis of cocaine dependence of any duration or severity randomly allocated to either acupuncture or sham or other control. We excluded studies of acupuncture methods and trials enrolling patients with polysubstance use or dependence. We abstracted data on study methodology and outcomes. We pooled the studies providing biochemical confirmation of cocaine abstinence. RESULTS: Nine studies enrolling 1747 participants met inclusion criteria; 7 provided details for biochemical confirmation of cocaine abstinence. On average, trials lost 50% of enrolled participants (range 0-63%). The pooled odds ratio estimating the effect of acupuncture on cocaine abstinence at the last reported time-point was 0.76 (95% CI, 0.45 to 1.27, P = 0.30, I2 = 30%, Heterogeneity P = 0.19). CONCLUSION: This systematic review and meta-analysis does not support the use of acupuncture for the treatment of cocaine dependence. However, most trials were hampered by large loss to follow up and the strength of the inference is consequently weakened.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recovery schools for improving behavioral and academic outcomes among students in recovery from substance use disorders: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 4;14(1):1-86. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.9. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131375 Free PMC article.
-
Auricular acupuncture in the treatment of cocaine/crack abuse: a review of the efficacy, the use of the National Acupuncture Detoxification Association protocol, and the selection of sham points.J Altern Complement Med. 2004 Dec;10(6):985-1000. doi: 10.1089/acm.2004.10.985. J Altern Complement Med. 2004. PMID: 15673993 Review.
-
Antipsychotics for cocaine or psychostimulant dependence: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials.J Clin Psychiatry. 2013 Dec;74(12):e1169-80. doi: 10.4088/JCP.13r08525. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24434105
-
Invasive acupuncture for gastroparesis after thoracic or abdominal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2023 Jun 26;13(6):e068559. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068559. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37369406 Free PMC article.
-
Limited evidence for non-pharmacological interventions for the relief of dry mouth.Evid Based Dent. 2014 Mar;15(1):25-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.ebd.6400989. Evid Based Dent. 2014. PMID: 24763174
Cited by
-
Effects of transcutaneous electric acupoint stimulation on drug use and responses to cue-induced craving: a pilot study.Chin Med. 2012 Jun 10;7(1):14. doi: 10.1186/1749-8546-7-14. Chin Med. 2012. PMID: 22682006 Free PMC article.
-
Auricular acupuncture for cocaine dependence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Jan 25;2006(1):CD005192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005192.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. PMID: 16437523 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of acupuncture research across components of the trauma spectrum response (tsr): a systematic review of reviews.Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 15;1:46. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-1-46. Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23067573 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of stimulant use disorder: A systematic review of reviews.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 18;15(6):e0234809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234809. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32555667 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic challenges in hepatitis C-infected injection drug using patients.Harm Reduct J. 2006 Nov 10;3:31. doi: 10.1186/1477-7517-3-31. Harm Reduct J. 2006. PMID: 17096852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cartwright WS. Cocaine medications, cocaine consumption and societal costs. Pharmacoeconomics. 2000;18:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Gunnarsson M, Fahlke C, Balldin J. [Adolescents who have tried illicit drugs and experienced psychiatric symptoms seldom seek professional help. A pilot study of 18-year old high school students in an urban district] Lakartidningen. 2004;101:1280–1282. - PubMed
-
- Nebelsieck H. [Recreational and designer drugs-the risks to heart and brain] MMW Fortschr Med. 2004;146:40–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous