A putative nucleoporin 96 Is required for both basal defense and constitutive resistance responses mediated by suppressor of npr1-1,constitutive 1
- PMID: 15772285
- PMCID: PMC1088004
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.104.029926
A putative nucleoporin 96 Is required for both basal defense and constitutive resistance responses mediated by suppressor of npr1-1,constitutive 1
Abstract
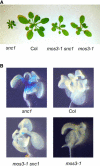
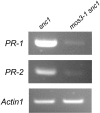
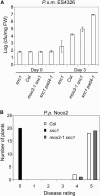
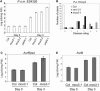
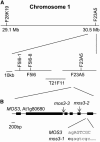
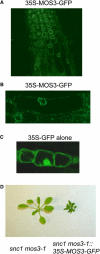
The Arabidopsis thaliana suppressor of npr1-1, constitutive 1 (snc1) mutant contains a gain-of-function mutation in a Toll Interleukin1 receptor-nucleotide binding-Leu-rich repeat-type resistance gene (R-gene), which leads to constitutive activation of disease resistance response against pathogens. In a screen for suppressors of snc1, a recessive mutation, designated mos3 (for modifier of snc1,3), was found to suppress the constitutive pathogenesis-related gene expression and resistance to virulent Pseudomonas syringae maculicola ES4326 and Peronospora parasitica Noco2 in snc1. In addition, mos3 is also compromised in resistance mediated by Resistance to Peronospora parasitica 4 (RPP4), Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv maculicola (RPM1), and Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae 4 (RPS4). Single mutant mos3 plants exhibited enhanced disease susceptibility to P. s. pv maculicola ES4326, suggesting that MOS3 is required for basal resistance to pathogens as well. mos3-1 was identified by map-based cloning, and it encodes a protein with high sequence similarity to human nucleoporin 96. Localization of the MOS3-green fluorescent protein fusion to the nuclear envelope further indicates that MOS3 may encode a nucleoporin, suggesting that nuclear and cytoplasmic trafficking plays an important role in both R-gene-mediated and basal disease resistance.
Figures
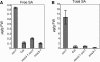


Similar articles
-
A gain-of-function mutation in a plant disease resistance gene leads to constitutive activation of downstream signal transduction pathways in suppressor of npr1-1, constitutive 1.Plant Cell. 2003 Nov;15(11):2636-46. doi: 10.1105/tpc.015842. Epub 2003 Oct 23. Plant Cell. 2003. PMID: 14576290 Free PMC article.
-
An importin alpha homolog, MOS6, plays an important role in plant innate immunity.Curr Biol. 2005 Jun 21;15(12):1129-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.022. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964279
-
Activation of an EDS1-mediated R-gene pathway in the snc1 mutant leads to constitutive, NPR1-independent pathogen resistance.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2001 Oct;14(10):1131-9. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.10.1131. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2001. PMID: 11605952
-
Characterization of a novel, defense-related Arabidopsis mutant, cir1, isolated by luciferase imaging.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002 Jun;15(6):557-66. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.6.557. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002. PMID: 12059104
-
Putative members of the Arabidopsis Nup107-160 nuclear pore sub-complex contribute to pathogen defense.Plant J. 2012 Jun;70(5):796-808. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04928.x. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22288649
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis TRANSCURVATA1 encodes NUP58, a component of the nucleopore central channel.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 28;8(6):e67661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067661. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840761 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a maize locus that modulates the hypersensitive defense response, using mutant-assisted gene identification and characterization.Genetics. 2010 Mar;184(3):813-25. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.111880. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Genetics. 2010. PMID: 20176981 Free PMC article.
-
OsWRKY62 and OsWRKY76 Interact with Importin α1s for Negative Regulation of Defensive Responses in Rice Nucleus.Rice (N Y). 2022 Feb 20;15(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12284-022-00558-4. Rice (N Y). 2022. PMID: 35184252 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear pore complex composition: a new regulator of tissue-specific and developmental functions.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;13(11):687-99. doi: 10.1038/nrm3461. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23090414 Review.
-
Quantitative phosphoproteomics identifies SnRK2 protein kinase substrates and reveals the effectors of abscisic acid action.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 2;110(27):11205-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308974110. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23776212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301, 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Austin, M.J., Muskett, P., Kahn, K., Feys, B.J., Jones, J.D., and Parker, J.E. (2002). Regulatory role of SGT1 in early R gene-mediated plant defenses. Science 295, 2077–2080. - PubMed
-
- Azevedo, C., Sadanandom, A., Kitagawa, K., Freialdenhoven, A., Shirasu, K., and Schulze-Lefert, P. (2002). The RAR1 interactor SGT1, an essential component of R gene-triggered disease resistance. Science 295, 2073–2076. - PubMed
-
- Belkhadir, Y., Nimchuk, Z., Hubert, D.A., Mackey, D., and Dangl, J.L. (2004. a). Arabidopsis RIN4 negatively regulates disease resistance mediated by RPS2 and RPM1 downstream or independent of the NDR1 signal modulator and is not required for the virulence functions of bacterial type III effectors AvrRpt2 or AvrRpm1. Plant Cell 16, 2822–2835. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

