Variation in the cortical area map of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J inbred mice predicts strain identity
- PMID: 15774010
- PMCID: PMC1079866
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-6-18
Variation in the cortical area map of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J inbred mice predicts strain identity
Abstract
Background: Recent discoveries suggest that arealization of the mammalian cortical sheet develops in a manner consonant with principles established for embryonic patterning of the body. Signaling centers release morphogens that determine regional growth and tissue identity by regulating regional expression of transcription factors. Research on mouse cortex has identified several candidate morphogens that affect anteroposterior or mediolateral cortical regionalization as well as mitogenesis. Inbred strains of laboratory mice can be exploited to study cortical area map formation if there are significant phenotypic differences with which to correlate gene polymorphism or expression data. Here we describe differences in the cortical area map of two commonly used inbred strains of laboratory mice, C57BL/6J and DBA/2J. Complete cortical hemispheres from adult mice were dissected and stained for the cytochrome oxidase enzyme in order to measure histochemically defined cortical areas.
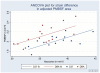
Results: C57BL/6J has the larger neocortex, relatively larger primary visual cortex (V1), but relatively smaller posterior medial barrel subfield of the primary somatosensory cortex (PMBSF). The sample of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice can be discriminated with 90% accuracy on the basis of these three size dimensions.
Conclusion: C57BL/6J and DBA/2J have markedly different cortical area maps, suggesting that inbred strains harbor enough phenotypic variation to encourage a forward genetic approach to understanding cortical development, complementing other approaches.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

