Endothelial vasodilator production by ovine uterine and systemic arteries: ovarian steroid and pregnancy control of ERalpha and ERbeta levels
- PMID: 15774511
- PMCID: PMC1464491
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.085753
Endothelial vasodilator production by ovine uterine and systemic arteries: ovarian steroid and pregnancy control of ERalpha and ERbeta levels
Abstract
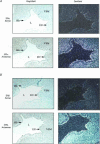
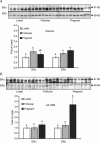
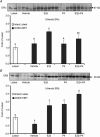
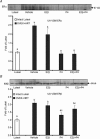
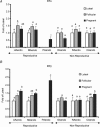
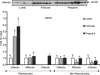
Pregnancy and the follicular phase are physiological states of elevated oestrogen levels and rises in uterine blood flow (UBF). The dramatic increase in utero-placental blood flow during gestation is required for normal fetal growth and development. Oestrogen exerts its vasodilatory effect by binding to its specific oestrogen receptors (ER) in target cells, resulting in increased expression and activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) to relax vascular smooth muscle (VSM). However, the regulation of endothelial versus VSM ERalpha and ERbeta expression in uterine arteries (UAs) during the ovarian cycle, pregnancy and with exogenous hormone replacement therapy (HRT) are currently unknown. ER mRNA and protein localization was determined by in situ hybridization (ISH) using 35S-labelled riboprobes and immunohistochemistry (IHC), respectively. UA endothelial (UAendo), UA VSM, omental artery endothelium (OA endo), and OA VSM proteins were isolated and ERalpha and ERbeta protein expression was determined by Western analysis. We observed by ISH and IHC that ERalpha and ERbeta mRNA and protein were localized in both UAendo and UA VSM. Immunoblot data demonstrated ovarian hormone specific regulation of ERalpha and ERbeta protein in UAendo and UA VSM. Compared to luteal phase sheep, both ERalpha and ERbeta levels in UAendo were elevated in follicular phase sheep. Whereas ERbeta was elevated by pregnancy in UAendo and UA VSM, ERalpha was not appreciably altered. eNOS was increased in UAendo from follicular and pregnant sheep. Ovariectomized ewes (OVEX) had substantially reduced UAendo ERbeta, but not UAendo ERalpha or OAendo ERalpha and ERbeta. In contrast, OVEX increased UA VSM ERalpha and ERbeta and decreased OA VSM ERalpha and ERbeta. Treatment with oestradiol-17beta (E2beta), but not progesterone or their combination, increased UAendo ERalpha levels. The reduced ERbeta in UAendo from OVEX ewes was reversed by E(2)beta and progesterone treatment. While ERalpha and eNOS were not elevated in any other reproductive or non-reproductive endothelia tested, ERbeta was augmented by pregnancy in uterine, mammary, placenta, and coronary artery endothelia. ERalpha and ERbeta mRNA and protein are expressed in UA endothelium with expression levels depending on the endocrine status of the animal, indicating UA endothelium is a target for oestrogen action in vivo, and that the two receptors appear to be differentially regulated in a spatial and temporal fashion with regard to the reproductive status or HRT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelial vasodilator production by uterine and systemic arteries. IV. Cyclooxygenase isoform expression during the ovarian cycle and pregnancy in sheep.Biol Reprod. 2000 Mar;62(3):781-8. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod62.3.781. Biol Reprod. 2000. PMID: 10684824
-
Pregnancy induces expression of cPLA2 in ovine uterine artery but not systemic artery endothelium.J Soc Gynecol Investig. 1999 Nov-Dec;6(6):301-6. doi: 10.1016/s1071-5576(99)00038-6. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 1999. PMID: 10643582
-
Uterine blood flow responses to ICI 182 780 in ovariectomized oestradiol-17beta-treated, intact follicular and pregnant sheep.J Physiol. 2005 May 15;565(Pt 1):71-83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.086439. Epub 2005 Mar 17. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15774510 Free PMC article.
-
Control of uterine and ovarian blood flow throughout the estrous cycle and pregnancy of ewes, sows and cows.J Anim Sci. 1982;55 Suppl 2:32-42. J Anim Sci. 1982. PMID: 6765316 Review.
-
Angiotensin II regulation of ovine fetoplacental artery endothelial functions: interactions with nitric oxide.J Physiol. 2005 May 15;565(Pt 1):59-69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.082420. Epub 2005 Mar 24. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15790666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uterine artery leptin receptors during the ovarian cycle and pregnancy regulate angiogenesis in ovine uterine artery endothelial cells†.Biol Reprod. 2017 Apr 1;96(4):866-876. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox008. Biol Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28339937 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in uterine artery endothelial cells by c-Jun/AP-1.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007 Dec 15;279(1-2):39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.08.017. Epub 2007 Sep 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17933457 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational hypoxia increases reactive oxygen species and inhibits steroid hormone-mediated upregulation of Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel function in uterine arteries.Hypertension. 2014 Aug;64(2):415-22. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03555. Epub 2014 May 27. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24866137 Free PMC article.
-
Uteroplacental Circulation in Normal Pregnancy and Preeclampsia: Functional Adaptation and Maladaptation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 11;22(16):8622. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168622. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen-responsive nitroso-proteome in uterine artery endothelial cells: role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and estrogen receptor-β.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Jan;227(1):146-59. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22712. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21374595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson SG, Hackshaw BT, Still JG, Greiss FC., Jr Uterine blood flow and its distribution after chronic estrogen and progesterone administration. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977;127:138–142. - PubMed
-
- Andersson C, Lydrup ML, Ferno M, Idvall I, Gustafsson J, Nilsson BO. Immunocytochemical demonstration of oestrogen receptor beta in blood vessels of the female rat. J Endocrinol. 2001;169:241–247. 10.1677/joe.0.1690241. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Batra S, Iosif S. Nuclear estrogen receptors in human uterine arteries. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1987;24:250–255. - PubMed
-
- Byers M, Kuiper GG, Gustafsson JA, Park-Sarge OK. Estrogen receptor-beta mRNA expression in rat ovary: down-regulation by gonadotropins. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:172–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

