Improved transduction of human sheep repopulating cells by retrovirus vectors pseudotyped with feline leukemia virus type C or RD114 envelopes
- PMID: 15774617
- PMCID: PMC1895126
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-11-4491
Improved transduction of human sheep repopulating cells by retrovirus vectors pseudotyped with feline leukemia virus type C or RD114 envelopes
Abstract
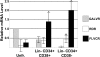
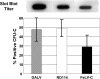
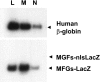
Gene therapy for hematopoietic diseases has been hampered by the low frequency of transduction of human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) with retroviral vectors pseudotyped with amphotropic envelopes. We hypothesized that transduction could be increased by the use of retroviral vectors pseudotyped with envelopes that recognize more abundant cellular receptors. The levels of mRNA encoding the receptors of the feline retroviruses, RD114 and feline leukemia virus type C (FeLV-C), were significantly higher than the level of gibbon ape leukemia virus (GaLV) receptor mRNA in cells enriched for human HSCs (Lin- CD34+ CD38-). We cotransduced human peripheral blood CD34+ cells with equivalent numbers of FeLV-C and GALV or RD114 and GALV-pseudotyped retroviruses for injection into fetal sheep. Analysis of DNA from peripheral blood and bone marrow from recipient sheep demonstrated that FeLV-C- or RD114-pseudotyped vectors were present at significantly higher levels than GALV-pseudotyped vectors. Analysis of individual myeloid colonies demonstrated that retrovirus vectors with FeLV-C and RD114 pseudotypes were present at 1.5 to 1.6 copies per cell and were preferentially integrated near known genes We conclude that the more efficient transduction of human HSCs with either FeLV-C- or RD114-pseudotyped retroviral particles may improve gene transfer in human clinical trials.
Figures
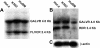


Similar articles
-
Direct comparison of RD114-pseudotyped versus amphotropic-pseudotyped retroviral vectors for transduction of rhesus macaque long-term repopulating cells.Mol Ther. 2003 Oct;8(4):611-7. doi: 10.1016/s1525-0016(03)00239-9. Mol Ther. 2003. PMID: 14529834
-
Lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with a modified RD114 envelope glycoprotein show increased stability in sera and augmented transduction of primary lymphocytes and CD34+ cells derived from human and nonhuman primates.Blood. 2002 Aug 1;100(3):823-32. doi: 10.1182/blood-2001-11-0042. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12130492
-
Sustained multilineage gene persistence and expression in dogs transplanted with CD34(+) marrow cells transduced by RD114-pseudotype oncoretrovirus vectors.Blood. 2001 Oct 1;98(7):2065-70. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.7.2065. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11567991
-
Gene transfer into marrow repopulating cells: comparison between amphotropic and gibbon ape leukemia virus pseudotyped retroviral vectors in a competitive repopulation assay in baboons.Blood. 1997 Dec 1;90(11):4638-45. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9373277
-
Development of gene therapy for blood disorders.Blood. 2008 May 1;111(9):4431-44. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-11-078121. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18441245 Review.
Cited by
-
Heme and FLVCR-related transporter families SLC48 and SLC49.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Apr-Jun;34(2-3):669-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.013. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23506900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FLVCR is necessary for erythroid maturation, may contribute to platelet maturation, but is dispensable for normal hematopoietic stem cell function.Blood. 2013 Oct 17;122(16):2903-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-10-465104. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24021674 Free PMC article.
-
Feline leukemia virus integrase and capsid packaging functions do not change the insertion profile of standard Moloney retroviral vectors.Gene Ther. 2010 Jun;17(6):799-804. doi: 10.1038/gt.2010.24. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 20237508 Free PMC article.
-
Transduction of human primitive repopulating hematopoietic cells with lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with various envelope proteins.Mol Ther. 2010 Jul;18(7):1310-7. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.48. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Mol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20372106 Free PMC article.
-
An all-feline retroviral packaging system for transduction of human cells.Hum Gene Ther. 2010 Aug;21(8):1019-27. doi: 10.1089/hum.2010.032. Hum Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 20222826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brenner S, Malech HL. Current developments in the design of onco-retrovirus and lentivirus vector systems for hematopoietic cell gene therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1640: 1-24. - PubMed
-
- Logan AC, Lutzko C, Kohn DB. Advances in lentiviral vector design for gene-modification of hematopoietic stem cells. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2002; 13: 429-436. - PubMed
-
- Hawley RG. Progress toward vector design for hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2001;1: 1-17. - PubMed
-
- Cavazzana-Calvo M, Hacein-Bey S, de Saint Basile G, et al. Gene therapy of human severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)-X1 disease. Science. 2000;288: 669-672. - PubMed
-
- Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Le Deist F, Carlier F, et al. Sustained correction of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency by ex vivo gene therapy. N Engl J Med. 2002;346: 1185-1193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

