Angiopoietin concentrations in diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 15774928
- PMCID: PMC1772595
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2004.049940
Angiopoietin concentrations in diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Background/aim: Angiopoietin 1 and 2 interact with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to promote angiogenesis in animal and in vitro models. Although VEGF concentrations are elevated, there is little information regarding angiopoietin concentration in the vitreous of patients with diabetic retinopathy.
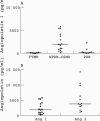
Methods: Angiopoietin concentrations were measured by luminescence immunoassay in vitreous samples from 17 patients with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) and clinically significant diabetic macular oedema (CSMO), 10 patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), and five patients with macular hole (controls) obtained at pars plana vitrectomy.
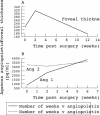
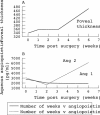
Results: Angiopoietin 1 concentrations were low in patients with macular hole (median 17 pg/ml) while in NPDR with CSMO they were 2002 pg/ml (range 289-5820 pg/ml) and in PDR 186 pg/ml (range 26-2292 pg/ml). Angiopoietin 2 concentrations in NPDR with CSMO were a median of 4000 pg/ml (range 1341-14 329 pg/ml). For both macular hole and PDR patients angiopoietin 2 was below the limit of detection.
Conclusions: Angiopoietin 2 concentration was twice that of angiopoietin 1 in NPDR with CSMO. Angiopoietin 2 is the natural antagonist of angiopoietin 1 which is thought to act as an anti-permeability agent. The predominance of angiopoietin 2 may allow VEGF induced retinal vascular permeability in patients with CSMO. The relatively low concentration of both angiopoietin 1 and 2 in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy may reflect the established nature of the neovascularisation in cases proceeding to vitrectomy.
Figures

References
-
- Adamis AP, Shima D, Tolentino M, et al. Inhibition of VEGF prevents retinal ischaemia-associated iris neovascularization in a primate. Arch Ophthalmol 1996;114:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Sato TN, Tozawa H, Deutsch U, et al. Distinct roles of receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature 1995;376:70–4. - PubMed
-
- Aiello LP, Avery R, Arrigg P, et al. Vascular endotheilal growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1480–7. - PubMed
-
- Koh GY, Kim I, Kwak HJ, et al. Biomedical significance of endothelial cell specific growth factor, angiopoietin. Expl Mol Med 2002;34:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Kim I, Moon S, Park SK, et al. Angiopoietin-1 regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Circ Res 2000;86:24–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
