Monitoring in chronic disease: a rational approach
- PMID: 15774996
- PMCID: PMC554914
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.330.7492.644
Monitoring in chronic disease: a rational approach
Figures
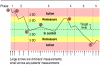
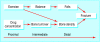
References
-
- Clague HW, Twum-Barima Y, Carruthers SG. An audit of requests for therapeutic drug monitoring of digoxin: problems and pitfalls. Ther Drug Monit 1983;5: 249-54. - PubMed
-
- Chen P, Tanasijevic MJ, Schoenenberger RA, Fiskio J, Kuperman GJ, Bates DW. A computer-based intervention for improving the appropriateness of antiepileptic drug level monitoring. Am J Clin Pathol 2003;119: 432-8. - PubMed
-
- Gibson PG, Wlodarczyk J, Hensley MJ, Murree-Allen K, Olson LG, Saltos N. Using quality-control analysis of peak expiratory flow recordings to guide therapy for asthma. Ann Intern Med 1995;123: 488-92. - PubMed
-
- Jannuzzi G, Cian P, Fattore C, Gatti G, Bartoli A, Monaco F, Perucca E. A multicenter randomized controlled trial on the clinical impact of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy. The Italian TDM Study Group in Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2000;41: 222-30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
