Monitoring agonist-promoted conformational changes of beta-arrestin in living cells by intramolecular BRET
- PMID: 15776020
- PMCID: PMC1299283
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400373
Monitoring agonist-promoted conformational changes of beta-arrestin in living cells by intramolecular BRET
Abstract
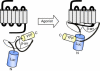
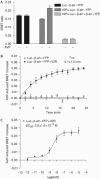
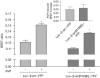
Recruitment of beta-arrestin (beta-arr) to agonist-stimulated G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) has a crucial role in controlling signalling efficacy and selectivity. When translocated to the receptor, beta-arr is believed to undergo important conformational rearrangement necessary for its downstream actions. To probe these changes in living cells, we constructed an intramolecular bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET)-based biosensor, in which beta-arr is sandwiched between the Renilla luciferase (Luc) and the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP). We show that the intramolecular BRET between Luc and YFP was significantly increased following GPCR activation, suggesting a conformational rearrangement bringing the amino terminus and carboxyl terminus of beta-arr in closer proximity. Kinetic analysis showed that this conformational change follows the initial beta-arr/receptor engagement. In addition to providing new insights into the agonist-induced conformational rearrangements of beta-arr in living cells, the double-brilliance beta-arr offers a universal biosensor for GPCR activation, allowing the study of native receptors in large-scale screening analysis.
Figures


References
-
- Andrews DL, Demidov AA (1999) Resonance Energy Transfer. Chichester, UK: Wiley
-
- Bertrand L, Parent S, Caron M, Legault M, Joly E, Angers S, Bouvier M, Brown M, Houle B, Menard L (2002) The BRET2/arrestin assay in stable recombinant cells: a platform to screen for compounds that interact with G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). J Receptor Signal Transduction Res 22: 533–541 - PubMed
-
- Charest PG, Bouvier M (2003) Palmitoylation of the V2 vasopressin receptor carboxyl tail enhances β-arrestin recruitment leading to efficient receptor endocytosis and ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem 278: 41541–41551 - PubMed
-
- Gurevich VV, Benovic JL (1993) Visual arrestin interaction with rhodopsin. Sequential multisite binding ensures strict selectivity toward light-activated phosphorylated rhodopsin. J Biol Chem 268: 11628–11638 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

