Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 2 years of treatment with the tumour necrosis factor alpha antibody infliximab
- PMID: 15778240
- PMCID: PMC1755223
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.033472
Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 2 years of treatment with the tumour necrosis factor alpha antibody infliximab
Abstract
Background: Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) treatment is clinically efficacious in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and leads to improvement of spinal inflammation, as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. It is unclear whether anti-TNF treatment affects chronic spinal changes in AS.
Objectives: To analyse the effect of infliximab on the radiographic course of AS over 2 years.
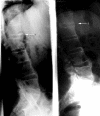
Methods: Complete sets of lateral radiographs of the cervical spine and lumbar spine were available from 82 patients from two sources: 41 patients (group 1) had been treated with infliximab (5 mg/kg/6 weeks) as part of a recent randomised controlled trial and 41 patients (group 2) were part of the early German AS cohort (GESPIC), without controlled interventions. Radiographs were obtained at baseline and after 2 years and scored by the modified Stokes AS Spinal Score (mSASSS).
Results: Patients in the infliximab group were older, had a longer disease duration, and more radiographic damage at baseline. The mean (SD) mSASSS change was 0.4 (2.7) and 0.7 (2.8) for groups 1 and 2, respectively (p = NS). Radiographic damage at baseline was a predictor for more radiographic progression. Patients with baseline damage who were treated with infliximab showed a trend for less radiographic progression. No correlations between clinical parameters and radiographic progression were found.
Conclusions: Patients with AS treated with infliximab had less radiographic progression after 2 years. Patients with prevalent radiographic damage are prone to develop more damage over time. Infliximab may decelerate radiographic progression in such patients. Larger studies are needed to prove that anti-TNF treatment inhibits structural damage.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 4 yrs of treatment with the anti-TNF-alpha antibody infliximab.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Sep;46(9):1450-3. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem166. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 17623745 Clinical Trial.
-
Continuous long-term anti-TNF therapy does not lead to an increase in the rate of new bone formation over 8 years in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Apr;73(4):710-5. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202698. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 23505240
-
Radiographic findings following two years of infliximab therapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Oct;58(10):3063-70. doi: 10.1002/art.23901. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18821688 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor α treatment on radiographic progression in patient with ankylosing spondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Mod Rheumatol. 2019 May;29(3):503-509. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2018.1525017. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Mod Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30220240
-
Infliximab: in ankylosing spondylitis.Drugs. 2005;65(9):1283-91; discussion 1292-4. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565090-00006. Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15916451 Review.
Cited by
-
Modified stoke ankylosing spondylitis spinal score as an outcome measure to assess the impact of treatment on structural progression in ankylosing spondylitis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Mar 1;58(3):388-400. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key128. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 29860356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological DMARDs and disease modification in axial spondyloarthritis: a review through the lens of causal inference.RMD Open. 2021 Jul;7(2):e001654. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001654. RMD Open. 2021. PMID: 34253683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs as Potential Disease-Modifying Medications in Axial Spondyloarthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr;72(4):518-528. doi: 10.1002/art.41164. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31705611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Early diagnosis of spondyloarthritis with special attention to the axial forms].Z Rheumatol. 2005 Nov;64(8):524-30. doi: 10.1007/s00393-005-0791-8. Z Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 16328756 Review. German.
-
Evaluation of dose reduction versus standard dosing for maintenance of remission in patients with spondyloarthritis and clinical remission with anti-TNF (REDES-TNF): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Aug 20;16:370. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0828-5. Trials. 2015. PMID: 26289076 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

