Membrane fluidity is a key modulator of membrane binding, insertion, and activity of 5-lipoxygenase
- PMID: 15778441
- PMCID: PMC1305639
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.056788
Membrane fluidity is a key modulator of membrane binding, insertion, and activity of 5-lipoxygenase
Abstract
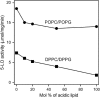
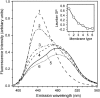
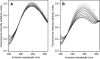
Mammalian 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) catalyzes conversion of arachidonic acid to leukotrienes, potent mediators of inflammation and allergy. Upon cell stimulation, 5-LO selectively binds to nuclear membranes and becomes activated, yet the mechanism of recruitment of 5-LO to nuclear membranes and the mode of 5-LO-membrane interactions are poorly understood. Here we show that membrane fluidity is an important determinant of membrane binding strength of 5-LO, penetration into the membrane hydrophobic core, and activity of the enzyme. The membrane binding strength and activity of 5-LO increase with the degree of lipid acyl chain cis-unsaturation and reach a plateau with 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonolyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (PAPC). A fraction of tryptophans of 5-LO penetrate into the hydrocarbon region of fluid PAPC membranes, but not into solid 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine membranes. Our data lead to a novel concept of membrane binding and activation of 5-LO, suggesting that arachidonic-acid-containing lipids, which are present in nuclear membranes at higher fractions than in other cellular membranes, may facilitate preferential membrane binding and insertion of 5-LO through increased membrane fluidity and may thereby modulate the activity of the enzyme. The data presented in this article and earlier data allow construction of a model for membrane-bound 5-LO, including the angular orientation and membrane insertion of the protein.
Figures
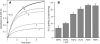


Similar articles
-
Modulation of human 5-lipoxygenase activity by membrane lipids.Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 23;43(46):14653-66. doi: 10.1021/bi048775y. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15544336
-
Interfacial Enzymes: Membrane Binding, Orientation, Membrane Insertion, and Activity.Methods Enzymol. 2017;583:197-230. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28063492
-
Nuclear localization of 5-lipoxygenase as a determinant of leukotriene B4 synthetic capacity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 14;100(21):12165-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2133253100. Epub 2003 Oct 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14530386 Free PMC article.
-
5-Lipoxygenase: regulation of expression and enzyme activity.Trends Biochem Sci. 2007 Jul;32(7):332-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007. PMID: 17576065 Review.
-
Development of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors--lessons from cellular enzyme regulation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2005 Aug 1;70(3):327-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.04.018. Biochem Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15907806 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of embedded endocannabinoids and their oxygenation by lipoxygenase on membrane properties.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012 May 16;3(5):386-92. doi: 10.1021/cn300016c. Epub 2012 Feb 24. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22860207 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Lipid Tail Length on the Organ Selectivity of mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticles.Nano Lett. 2024 Oct 7;24(41):12758-67. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c02566. Online ahead of print. Nano Lett. 2024. PMID: 39373269 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative Effect of 7-Ketositosterol in Breast and Liver Cancer Cells: Possible Impact on Ceramide, Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases, and Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathways.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 1;17(7):860. doi: 10.3390/ph17070860. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065711 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of lipid chemistry on membrane fluidity: tail and headgroup interactions.Biophys J. 2006 Nov 15;91(10):3727-35. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.084590. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16950848 Free PMC article.
-
Location, location, location: compartmentalization of early events in leukotriene biosynthesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 13;285(33):25109-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R110.125880. Epub 2010 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20507998 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramovitz, M., E. Wong, M. E. Cox, C. D. Richardson, C. Li, and P. J. Vickers. 1993. 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein stimulates the utilization of arachidonic acid by 5-lipoxygenase. Eur. J. Biochem. 215:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Albi, E., M. L. Tomassoni, and M. Viola-Magni. 1997. Effect of lipid composition on rat liver nuclear membrane fluidity. Cell Biochem. Funct. 3:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brock, T. G., R. W. McNish, and M. Peters-Golden. 1995. Translocation and leukotriene synthetic capacity of nuclear 5-lipoxygenase in rat basophilic leukemia cells and alveolar macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 270:21652–21658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

