A surfactant protein C precursor protein BRICHOS domain mutation causes endoplasmic reticulum stress, proteasome dysfunction, and caspase 3 activation
- PMID: 15778495
- PMCID: PMC2715321
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0009OC
A surfactant protein C precursor protein BRICHOS domain mutation causes endoplasmic reticulum stress, proteasome dysfunction, and caspase 3 activation
Abstract
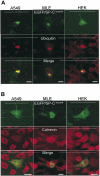
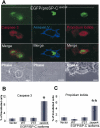
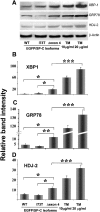
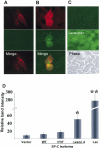
BRICHOS is a domain found in several proteins consisting of approximately 100 amino acids with sequence and structural similarities. Mutations in BRICHOS domain have been associated with both degenerative and proliferative diseases in several nonpulmonary organs, although the pathogenic mechanisms are largely undefined. Recently, several mutations in surfactant protein C (SP-C) mapping to the BRICHOS domain located within the proprotein (proSP-C) have been linked to interstitial lung diseases. In vitro expression of one of these BRICHOS mutants, the exon 4 deletion (hSP-CDeltaexon4), promotes a dominant-negative perinuclear aggregation of the protein. The present study characterizes the trafficking behavior and pathogenic consequences resulting from hSP-CDeltaexon4 expression. Time-lapse and co-localization microscopy studies demonstrated enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)/hSP-CDeltaexon4 expression in calnexin-positive (endoplasmic reticulum [ER]) compartment with subsequent time- and concentration-dependent development of ubiquitinated perinuclear inclusion bodies followed by apoptosis. Compared with controls, EGFP/hSP-CDeltaexon4 promoted upregulation of multiple ER stress species, activated caspase 3, and induced annexin V binding. Furthermore, in GFP-u cells, hSP-CDeltaexon4 directly inhibited proteasome activity. These results support a model whereby proSP-C BRICHOS mutations induce a dynamic toxic gain-of-function, causing apoptotic cell death both by early ER accumulation leading to an exaggerated unfolded protein response and by enhanced deposition of cellular aggregates associated with proteasome dysfunction.
Figures







References
-
- Beers M. Molecular processing and cellular metabolism of surfactant protein C. In: Rooney SA, editor. Lung surfactant: cellular and molecular processing. Austin: R.G. Landes; 1998. pp. 93–124.
-
- Johansson J. Structure and properties of surfactant protein C. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998;1408:161–172. - PubMed
-
- Weaver TE. Synthesis, processing and secretion of surfactant proteins B and C. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998;1408:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez-Pulido L, Devos D, Valencia A. BRICHOS: a conserved domain in proteins associated with dementia, respiratory distress and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 2002;27:329–332. - PubMed
-
- Vidal R, Frangione B, Rostagno A, Mead S, Revesz T, Plant G, Ghiso J. A stop-codon mutation in the BRI gene associated with familial British dementia. Nature 1999;399:776–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

