A gene(s) for all-trans-retinoic acid-induced forelimb defects mapped and confirmed to murine chromosome 11
- PMID: 15781699
- PMCID: PMC1449723
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.038620
A gene(s) for all-trans-retinoic acid-induced forelimb defects mapped and confirmed to murine chromosome 11
Abstract
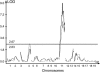
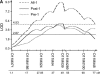
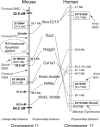
All-trans-retinoic acid (RA) induces various anatomical limb dysmorphologies in mice dependent on the time of exposure. During early limb development, RA induces forelimb ectrodactyly (digital absence) with varying susceptibilities for different inbred mouse strains; C57BL/6N are highly susceptible while SWV are resistant. To isolate the genetic basis of this defect, a full-genome scan was performed in 406 backcross fetuses of F(1) males to C57BL/6N females. Fetuses were exposed via a maternal injection of 75 mg of RA per kilogram of body weight on gestational day 9.25. The genome-wide analysis revealed significant linkage to a chromosome 11 locus near D11Mit39 with a maximum LOD score of 9.0 and to a chromosome 4 locus near D4Mit170. An epistatic interaction was detected between loci on chromosome 11 (D11Mit39) and chromosome 18 (D18Mit64). Linkage to the chromosome 11 locus (D11Mit39) was confirmed in RA-treated backcross fetuses of F(1) females to C57BL/6N males. Loci associated with bone density/mass in both human and mouse were previously detected in the same region, suggesting a mechanistic linkage with bone homeostasis. The human syntenic region of this locus has been previously linked to Meckel syndrome; the phenotype includes postaxial polydactyly, an ectopic digital defect hypothesized to be induced by a common molecular pathway with ectrodactyly.
Figures
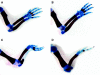

References
-
- Bateson, W., 1909 Mendel's Principles of Heredity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
-
- Beamer, W. G., L. R. Donahue, C. J. Rosen and D. J. Baylink, 1996. Genetic variability in adult bone density among inbred strains of mice. Bone 18: 397–403. - PubMed
-
- Beamer, W. G., K. L. Shultz, L. R. Donahue, G. A. Churchill, S. Sen et al., 2001. Quantitative trait loci for femoral and lumbar vertebral bone mineral density in C57BL/6J and C3H/HeJ inbred strains of mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 16: 1195–1206. - PubMed
-
- Benes, H., R. S. Weinstein, W. Zheng, J. J. Thaden, R. L. Jilka et al., 2000. Chromosomal mapping of osteopenia-associated quantitative trait loci using closely related mouse strains. J. Bone Miner. Res. 15: 626–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

