Deleted in colorectal cancer binding netrin-1 mediates cell substrate adhesion and recruits Cdc42, Rac1, Pak1, and N-WASP into an intracellular signaling complex that promotes growth cone expansion
- PMID: 15788770
- PMCID: PMC6725078
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1920-04.2005
Deleted in colorectal cancer binding netrin-1 mediates cell substrate adhesion and recruits Cdc42, Rac1, Pak1, and N-WASP into an intracellular signaling complex that promotes growth cone expansion
Abstract
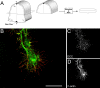
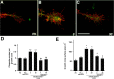
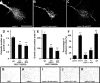
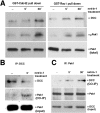
Extracellular cues direct axon extension by regulating growth cone morphology. The netrin-1 receptor deleted in colorectal cancer (DCC) is required for commissural axon extension to the floor plate in the embryonic spinal cord. Here we demonstrate that challenging embryonic rat spinal commissural neurons with netrin-1, either in solution or as a substrate, causes DCC-dependent increases in growth cone surface area and filopodia number, which we term growth cone expansion. We provide evidence that DCC influences growth cone morphology by at least two mechanisms. First, DCC mediates an adhesive interaction with substrate-bound netrin-1. Second, netrin-1 binding to DCC recruits an intracellular signaling complex that directs the organization of actin. We show that netrin-1-induced growth cone expansion requires Cdc42 (cell division cycle 42), Rac1 (Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1), Pak1 (p21-activated kinase), and N-WASP (neuronal Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein) and that the application of netrin-1 rapidly activates Cdc42, Rac1, and Pak1. Furthermore, netrin-1 recruits Cdc42, Rac1, Pak1, and N-WASP into a complex with the intracellular domain of DCC and Nck1. These findings suggest that DCC influences growth cone morphology by acting both as a transmembrane bridge that links extracellular netrin-1 to the actin cytoskeleton and as the core of a protein complex that directs the organization of actin.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The netrin-1 receptor DCC promotes filopodia formation and cell spreading by activating Cdc42 and Rac1.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002 Jan;19(1):1-17. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2001.1075. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11817894
-
FLIM FRET Visualization of Cdc42 Activation by Netrin-1 in Embryonic Spinal Commissural Neuron Growth Cones.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 2;11(8):e0159405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159405. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27482713 Free PMC article.
-
Trio mediates netrin-1-induced Rac1 activation in axon outgrowth and guidance.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;28(7):2314-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00998-07. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18212043 Free PMC article.
-
[Netrin-1 and axonal guidance: signaling and asymmetrical translation].Med Sci (Paris). 2007 Mar;23(3):311-5. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2007233311. Med Sci (Paris). 2007. PMID: 17349294 Review. French.
-
Netrins and their receptors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;621:17-31. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-76715-4_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18269208 Review.
Cited by
-
Central nervous system functions of PAK protein family: from spine morphogenesis to mental retardation.Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Aug;34(1):67-80. doi: 10.1385/mn:34:1:67. Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17003522 Review.
-
Regulation of early neurite morphogenesis by the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1.J Neurosci. 2009 Jul 15;29(28):8946-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2030-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19605632 Free PMC article.
-
PAK-PIX interactions regulate adhesion dynamics and membrane protrusion to control neurite outgrowth.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 1;126(Pt 5):1122-33. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112607. Epub 2013 Jan 15. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23321640 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Netrin-1 in glioblastoma stem-like cells inhibits growth, invasion, and angiogenesis.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):14949-14960. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5314-5. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27651158
-
NCK1 Modulates Neuronal Actin Dynamics and Promotes Dendritic Spine, Synapse, and Memory Formation.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 8;43(6):885-901. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0495-21.2022. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36535770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagrodia S, Cerione RA (1999) Pak to the future. Trends Cell Biol 9: 350-355. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia S, Taylor SJ, Creasy CL, Chernoff J, Cerione RA (1995) Identification of a mouse p21Cdc42/Rac activated kinase. J Biol Chem 270: 22731-22737. - PubMed
-
- Banzai Y, Miki H, Yamaguchi H, Takenawa T (2000) Essential role of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein in neurite extension in PC12 cells and rat hippocampal primary culture cells. J Biol Chem 275: 11987-11992. - PubMed
-
- Bentley D, O'Connor TP (1994) Cytoskeletal events in growth cone steering. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4: 43-48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
