In vivo activation of a mutant mu-opioid receptor by naltrexone produces a potent analgesic effect but no tolerance: role of mu-receptor activation and delta-receptor blockade in morphine tolerance
- PMID: 15788780
- PMCID: PMC5764089
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0332-05.2005
In vivo activation of a mutant mu-opioid receptor by naltrexone produces a potent analgesic effect but no tolerance: role of mu-receptor activation and delta-receptor blockade in morphine tolerance
Abstract
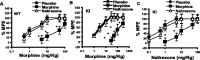
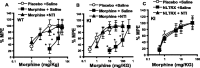
Opioid analgesics are the standard therapeutic agents for the treatment of pain, but their prolonged use is limited because of the development of tolerance and dependence. Recently, we reported the development of a mu-opioid receptor knock-in (KI) mouse in which the mu-opioid receptor was replaced by a mutant receptor (S196A) using a homologous recombination gene-targeting strategy. In these animals, the opioid antagonist naltrexone elicited antinociceptive effects similar to those of partial agonists acting in wild-type (WT) mice; however, development of tolerance and physical dependence were greatly reduced. In this study, we test the hypothesis that the failure of naltrexone to produce tolerance in these KI mice is attributable to its simultaneous inhibition of delta-opioid receptors and activation of mu-opioid receptors. Simultaneous implantation of a morphine pellet and continuous infusion of the delta-opioid receptor antagonist naltrindole prevented tolerance development to morphine in both WT and KI animals. Moreover, administration of SNC-80 [(+)-4-[(alphaR)-alpha-((2S,5R)-4-allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-methoxybenzyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide], a delta agonist, in the naltrexone-pelleted KI animals resulted in a dose-dependent induction in tolerance development to both morphine- and naltrexone-induced analgesia. We conclude that although simultaneous activation of both mu- and delta-opioid receptors results in tolerance development, mu-opioid receptor activation in conjunction with delta-opioid receptor blockade significantly attenuates the development of tolerance.
Figures


References
-
- Abdelhamid EE, Sultana M, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE (1991) Selective blockage of δ opioid receptors prevents the development of morphine tolerance and dependence in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258: 299-303. - PubMed
-
- Chen YL, Law PY, Loh HH (2004) Inhibition of akt/protein kinase B signaling by naltrindole in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 64: 8723-8730. - PubMed
-
- Ellison NM (1993) Opioid analgesics for cancer pain: toxicities and their treatment. In: Cancer pain (Patt RB, ed), pp 185-194. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott.
-
- Fang FG, Fields HL, Lee NM (1986) Action at the μ receptor is sufficient to explain the supraspinal analgesic effect of opiates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238: 1039-1044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA012104/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA00564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- KO2 DA015349/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA01583/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA12104/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007097/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA015349/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA001583/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA 11806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32DA07097/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- KO5-DA70554/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA070554/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA11806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA033881/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
