Persistent shedding of viable SARS-CoV in urine and stool of SARS patients during the convalescent phase
- PMID: 15789222
- PMCID: PMC7088045
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-005-1299-5
Persistent shedding of viable SARS-CoV in urine and stool of SARS patients during the convalescent phase
Abstract
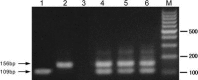
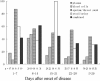
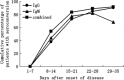
In order to further the present knowledge of the emerging severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV), 486 different specimens from 54 patients with a clinical diagnosis of SARS were investigated for the presence of viral RNA, and 314 plasma specimens of 73 patients were examined for IgM and IgG antibodies specific against SARS-CoV using an indirect ELISA. Viral RNA was detectable in 28 of the 54 patients tested. Cumulative data showed that 67 of the 73 SARS patients demonstrated seroconversion by week 5 of illness. In contrast, only 1 of 278 healthy subjects enrolled in the study was found to be positive for the IgG antibody. Coexistence of viral RNA in plasma and specific antibodies was simultaneously observed over three consecutive weeks in two critical cases. In three convalescent patients in particular, cultivable SARS-CoV was detected in stool or urine specimens for longer than 4 weeks (29-36 days). These findings suggest that SARS-CoV may remain viable in the excretions of convalescent patients.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (2004) Summary of probable SARS with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. Available at: http://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/table2004_04_21/en/. Cited 8 May 2004
-
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, Becker S, Rabenau H, Panning M, Kolesnikova L, Fouchier RA, Berger A, Burguiere AM, Cinatl J, Eickmann M, Escriou N, Grywna K, Kramme S, Manuguerra JC, Muller S, Rickerts V, Sturmer M, Vieth S, Klenk HD, Osterhaus AD, Schmitz H, Doerr HW. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030747. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, Tong S, Urbani C, Comer JA, Lim W, Rollin PE, Dowell SF, Ling AE, Humphrey CD, Shieh WJ, Guarner J, Paddock CD, Rota P, Fields B, DeRisi J, Yang JY, Cox N, Hughes JM, LeDuc JW, Bellini WJ, Anderson LJ, SARS Working Group A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030781. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marra MA, Jones SJ, Astell CR, Holt RA, Brooks-Wilson A, Butterfield YS, Khattra J, et al. The genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

