GeneKeyDB: a lightweight, gene-centric, relational database to support data mining environments
- PMID: 15790402
- PMCID: PMC1274265
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-72
GeneKeyDB: a lightweight, gene-centric, relational database to support data mining environments
Abstract
Background: The analysis of biological data is greatly enhanced by existing or emerging databases. Most existing databases, with few exceptions are not designed to easily support large scale computational analysis, but rather offer exclusively a web interface to the resource. We have recognized the growing need for a database which can be used successfully as a backend to computational analysis tools and pipelines. Such database should be sufficiently versatile to allow easy system integration.
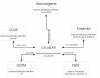
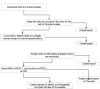
Results: GeneKeyDB is a gene-centered relational database developed to enhance data mining in biological data sets. The system provides an underlying data layer for computational analysis tools and visualization tools. GeneKeyDB relies primarily on existing database identifiers derived from community databases (NCBI, GO, Ensembl, et al.) as well as the known relationships among those identifiers. It is a lightweight, portable, and extensible platform for integration with computational tools and analysis environments.
Conclusion: GeneKeyDB can enable analysis tools and users to manipulate the intersections, unions, and differences among different data sets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MILANO--custom annotation of microarray results using automatic literature searches.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Jan 20;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-12. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15661078 Free PMC article.
-
Atlas - a data warehouse for integrative bioinformatics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Feb 21;6:34. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-34. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15723693 Free PMC article.
-
GeneNotes--a novel information management software for biologists.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Feb 1;6:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-20. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15686593 Free PMC article.
-
Automation of in-silico data analysis processes through workflow management systems.Brief Bioinform. 2008 Jan;9(1):57-68. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbm056. Epub 2007 Dec 2. Brief Bioinform. 2008. PMID: 18056132 Review.
-
Evolution of web services in bioinformatics.Brief Bioinform. 2005 Jun;6(2):178-88. doi: 10.1093/bib/6.2.178. Brief Bioinform. 2005. PMID: 15975226 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of prostate cancer clinical data using an ontology.J Biomed Inform. 2009 Dec;42(6):1035-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2009.05.007. Epub 2009 Jun 2. J Biomed Inform. 2009. PMID: 19497389 Free PMC article.
-
DNA copy number aberrations in small-cell lung cancer reveal activation of the focal adhesion pathway.Oncogene. 2010 Dec 2;29(48):6331-42. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.362. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20802517 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking-related genomic signatures in non-small cell lung cancer.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Dec 1;178(11):1164-72. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200801-142OC. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18776155 Free PMC article.
-
PAZAR: a framework for collection and dissemination of cis-regulatory sequence annotation.Genome Biol. 2007;8(10):R207. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-10-r207. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 17916232 Free PMC article.
-
SynaptomeDB: an ontology-based knowledgebase for synaptic genes.Bioinformatics. 2012 Mar 15;28(6):897-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts040. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22285564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brooksbank C, Camon E, Harris MA, Magrane M, Martin MJ, Mulder N, O'Donovan C, Parkinson H, Tuli MA, Apweiler R, Birney E, Brazma A, Henrick K, Lopez R, Stoesser G, Stoehr P, Cameron G. The European Bioinformatics Institute's data resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:43–50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

