Psychometric properties of the Flemish translation of the NEECHAM Confusion Scale
- PMID: 15792498
- PMCID: PMC1079887
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-5-16
Psychometric properties of the Flemish translation of the NEECHAM Confusion Scale
Abstract
Background: Determination of a patient's cognitive status by use of a valid and reliable screening instrument is of major importance as early recognition and accurate diagnosis of delirium is necessary for effective management. This study determined the reliability, validity and diagnostic value of the Flemish translation of the NEECHAM Confusion Scale.
Methods: A sample of 54 elderly hip fracture patients with a mean age of 80.9 years (SD = 7.85) were included. To test the psychometric properties of the NEECHAM Confusion Scale, performance on the NEECHAM was compared to the Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) and the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), by using aggregated data based on 5 data collection measurement points (repeated measures). The CAM and MMSE served as gold standards.
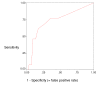
Results: The alpha coefficient for the total NEECHAM score was high (0.88). Principal components analysis yielded a two-component solution accounting for 70.8% of the total variance. High correlations were found between the total NEECHAM scores and total MMSE (0.75) and total CAM severity scores (-0.73), respectively. Diagnostic values using the CAM algorithm as gold standard showed 76.9% sensitivity, 64.6% specificity, 13.5% positive and 97.5% negative predictive values, respectively.
Conclusion: This validation of the Flemish version of the NEECHAM Confusion Scale adds to previous evidence suggesting that this scale holds promise as a valuable screening instrument for delirium in clinical practice. Further validation studies in diverse clinical populations; however, are needed.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington D.C.: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Gustafson Y, Brännström B, Norberg A, Bucht G, Winblad B. Underdiagnosis and poor documentation of acute confusional states in elderly fracture patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991;39:760–765. - PubMed
-
- Inouye SK. Delirium in hospitalized elderly patients: Recognition, evaluation, and management. Conn Med. 1993;57:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Lipowski ZJ. Delirium in the elderly patient. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:578–582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources