Chronic inflammatory pain leads to increased blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein alterations
- PMID: 15792985
- PMCID: PMC4638185
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01288.2004
Chronic inflammatory pain leads to increased blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein alterations
Abstract
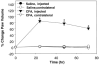
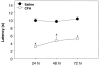
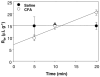
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) maintains brain homeostasis by limiting entry of substances to the central nervous system through interaction of transmembrane and intracellular proteins that make up endothelial cell tight junctions (TJs). Recently it was shown that the BBB can be modulated by disease pathologies including inflammatory pain. This study examined the effects of chronic inflammatory pain on the functional and molecular integrity of the BBB. Inflammatory pain was induced by injection of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) into the right plantar hindpaw in female Sprague-Dawley rats under halothane anesthesia; control animals were injected with saline. Edema and hyperalgesia were assessed by plethysmography and infrared paw-withdrawal latency. At 72 h postinjection, significant edema formation and hyperalgesia were noted in the CFA-treated rats. Examination of permeability of the BBB by in situ perfusion of [14C]sucrose while rats were under pentobarbital anesthesia demonstrated that CFA treatment significantly increased brain sucrose uptake. Western blot analysis of BBB TJ proteins showed no change in expression of zonula occludens-1 (an accessory protein) or actin (a cytoskeletal protein) with CFA treatment. Expression of the transmembrane TJ proteins occludin and claudin-3 and -5 significantly changed with CFA treatment with a 60% decrease in occludin, a 450% increase in claudin-3, and a 615% increase in claudin-5 expression. This study demonstrates that during chronic inflammatory pain, alterations in BBB function are associated with changes in specific transmembrane TJ proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Bazzoni G, Dejana E. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:869–901. - PubMed
-
- Brightman MW, Kadota Y. Nonpermeable and permeable vessels of the brain. NIDA Res Monogr. 1992;120:87–107. - PubMed
-
- Butt AM. Effect of inflammatory agents on electrical resistance across the blood-brain barrier in pial microvessels of anaesthetized rats. Brain Res. 1995;696:145–150. - PubMed
-
- Chen SP, Zhou B, Willis BC, Sandoval AJ, Liebler JM, Kim KJ, Ann DK, Crandall ED, Borok Z. Effects of transdifferentiation and EGF on claudin isoform expression in alveolar epithelial cells. J Appl Physiol. 2005;98:322–328. - PubMed
-
- Coyne CB, Gambling TM, Boucher RC, Carson JL, Johnson LG. Role of claudin interactions in airway tight junctional permeability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;285:L1166–L1178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

