A protein folding pathway with multiple folding intermediates at atomic resolution
- PMID: 15793003
- PMCID: PMC555603
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0501372102
A protein folding pathway with multiple folding intermediates at atomic resolution
Abstract
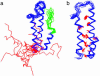
Using native-state hydrogen-exchange-directed protein engineering and multidimensional NMR, we determined the high-resolution structure (rms deviation, 1.1 angstroms) for an intermediate of the four-helix bundle protein: Rd-apocytochrome b562. The intermediate has the N-terminal helix and a part of the C-terminal helix unfolded. In earlier studies, we also solved the structures of two other folding intermediates for the same protein: one with the N-terminal helix alone unfolded and the other with a reorganized hydrophobic core. Together, these structures provide a description of a protein folding pathway with multiple intermediates at atomic resolution. The two general features for the intermediates are (i) native-like backbone topology and (ii) nonnative side-chain interactions. These results have implications for important issues in protein folding studies, including large-scale conformation search, -value analysis, and computer simulations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Specific non-native hydrophobic interactions in a hidden folding intermediate: implications for protein folding.Biochemistry. 2003 Nov 4;42(43):12461-5. doi: 10.1021/bi035561s. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14580191
-
An on-pathway hidden intermediate and the early rate-limiting transition state of Rd-apocytochrome b562 characterized by protein engineering.J Mol Biol. 2005 Sep 30;352(4):757-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.07.057. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16125200
-
Detection and structure determination of an equilibrium unfolding intermediate of Rd-apocytochrome b562: native fold with non-native hydrophobic interactions.J Mol Biol. 2004 Nov 5;343(5):1477-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.099. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15491625
-
Folding of apomyoglobin: Analysis of transient intermediate structure during refolding using quick hydrogen deuterium exchange and NMR.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2017;93(1):10-27. doi: 10.2183/pjab.93.002. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28077807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMR as a tool to identify and characterize protein folding intermediates.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013 Mar;531(1-2):90-9. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 22982558 Review.
Cited by
-
Cysteine-based protein folding modulators for trapping intermediates and misfolded forms.RSC Adv. 2022 Sep 21;12(41):26658-26664. doi: 10.1039/d2ra04044a. eCollection 2022 Sep 16. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36275147 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Folding-How and Why: By Hydrogen Exchange, Fragment Separation, and Mass Spectrometry.Annu Rev Biophys. 2016 Jul 5;45:135-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-062215-011121. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Annu Rev Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27145881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing the folding intermediate of Rd-apocyt b562 by protein engineering and infrared T-jump.Protein Sci. 2007 Jun;16(6):1176-83. doi: 10.1110/ps.062505607. Epub 2007 May 1. Protein Sci. 2007. PMID: 17473017 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal use of data in parallel tempering simulations for the construction of discrete-state Markov models of biomolecular dynamics.J Chem Phys. 2011 Jun 28;134(24):244108. doi: 10.1063/1.3592153. J Chem Phys. 2011. PMID: 21721613 Free PMC article.
-
Structural gymnastics of multifunctional metamorphic proteins.Biophys Rev. 2011 Sep;3(3):143. doi: 10.1007/s12551-011-0053-8. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Biophys Rev. 2011. PMID: 28510063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim, P. S. & Baldwin, R. L. (1982) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 51, 459–489. - PubMed
-
- Kim, P. S. & Baldwin, R. L. (1990) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 631–660. - PubMed
-
- Englander, S. W. & Mayne, L. (1992) Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 21, 243–265. - PubMed
-
- Matthews, C. R. (1993) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62, 653–683. - PubMed
-
- Ptitsyn, O. B. (1995) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 5, 74–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

