Transforming growth factor-{beta}1 modulates responses of CD34+ cord blood cells to stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCL12
- PMID: 15797995
- PMCID: PMC1895172
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-4145
Transforming growth factor-{beta}1 modulates responses of CD34+ cord blood cells to stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCL12
Abstract
Disruption of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1/CXCL12 [CXC chemokine ligand 12]) interaction leads to mobilization of stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow to circulation. However, prolonged exposure of CD34+ cells to SDF-1 desensitizes them to SDF-1. So how do cells remain responsive to SDF-1 in vivo when they are continuously exposed to SDF-1? We hypothesized that one or more mechanisms mediated by cytokines exist that could modulate SDF-1 responsiveness of CD34+ cells and the desensitization process. We considered transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) a possible candidate, since TGF-beta1 has effects on CD34+ cells and is produced by stromal cells, which provide niches for maintenance and proliferation of stem/progenitor cells. TGF-beta1 significantly restored SDF-1-induced chemotaxis and sustained adhesion responses in cord blood CD34+ cells preexposed to SDF-1. Effects of TGF-beta1 were dependent on the dose and duration of TGF-beta1 pretreatment. Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (Erk1)/Erk2 was implicated in TGF-beta1 modulation of migratory and adhesion responses to SDF-1. Our results indicate that low levels of TGF-beta1 can modulate SDF-1 responsiveness of CD34+ cells and thus may facilitate SDF-1-mediated retention and nurturing of stem/progenitor cells in bone marrow.
Figures
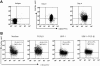


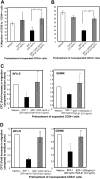

 ) of the adhesion assay. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in absence of SDF-1 stimulation (basal adhesion) for respective pretreatment and **P < .05 compared with cells pretreated with SDF-1 alone. (B) CD34+ cells pretreated under various conditions were preincubated with anti–VLA-4 and anti–VLA-5 antibodies and assayed in adhesion assay. The cells were plated in fibronectin-coated plates and stimulated with SDF-1 for 30 minutes. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in the absence of antibodies. (C) Nonexpanded CD34+-enriched cord blood cells were cultured in medium (containing 20% FCS) alone or along with TGF-β1 (0.5 ng/mL), SDF-1 (200 ng/mL), or SDF-1 (200 ng/mL) and TGF-β1 (0.5 ng/mL) for 24 hours. These cells were then assayed for their ability to bind to fibronectin in the absence or presence of 200 ng/mL SDF-1 for 2 minutes (transient response) and 30 minutes (sustained response). Nonadherent cells were removed, and adherent cells were quantified as described in “Materials and methods.” Data represent the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in absence of SDF-1 stimulation (basal adhesion) for respective pretreatment. (D) Fresh CD34+ cells pretreated under various conditions for 24 hours were preincubated with anti–VLA-4 antibody and assayed in adhesion assay as described in “Materials and methods.” Data represent mean ± SEM of 1 experiment. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in absence of antibodies.
) of the adhesion assay. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in absence of SDF-1 stimulation (basal adhesion) for respective pretreatment and **P < .05 compared with cells pretreated with SDF-1 alone. (B) CD34+ cells pretreated under various conditions were preincubated with anti–VLA-4 and anti–VLA-5 antibodies and assayed in adhesion assay. The cells were plated in fibronectin-coated plates and stimulated with SDF-1 for 30 minutes. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in the absence of antibodies. (C) Nonexpanded CD34+-enriched cord blood cells were cultured in medium (containing 20% FCS) alone or along with TGF-β1 (0.5 ng/mL), SDF-1 (200 ng/mL), or SDF-1 (200 ng/mL) and TGF-β1 (0.5 ng/mL) for 24 hours. These cells were then assayed for their ability to bind to fibronectin in the absence or presence of 200 ng/mL SDF-1 for 2 minutes (transient response) and 30 minutes (sustained response). Nonadherent cells were removed, and adherent cells were quantified as described in “Materials and methods.” Data represent the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in absence of SDF-1 stimulation (basal adhesion) for respective pretreatment. (D) Fresh CD34+ cells pretreated under various conditions for 24 hours were preincubated with anti–VLA-4 antibody and assayed in adhesion assay as described in “Materials and methods.” Data represent mean ± SEM of 1 experiment. *P < .05 compared with adhesion response in absence of antibodies.References
-
- Osawa M, Hanada K, Hamada H, Nakauchi H. Long-term lymphohematopoietic reconstitution by a single CD34-low/negative hematopoietic stem cell. Science. 1996;273: 242-245. - PubMed
-
- Lapidot T, Kollet O. The essential roles of the chemokine SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4 in human stem cell homing and repopulation of transplanted immune-deficient NOD/SCID and NOD/SCID/B2m(null) mice. Leukemia. 2002;16: 1992-2003. - PubMed
-
- Christopherson KW, Broxmeyer HE. Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell homing, engraftment, and mobilization in the context of CXCL12/SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. In: Broxmeyer HE, ed. Cord Blood Biology, Immunology, Banking, and Clinical Transplantation. Bethesda, MD: AABB Press; 2004: 65-86.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

