Role of protein and amino acids in the pathophysiology and treatment of sarcopenia
- PMID: 15798081
- PMCID: PMC3192454
- DOI: 10.1080/07315724.2005.10719455
Role of protein and amino acids in the pathophysiology and treatment of sarcopenia
Abstract
Sarcopenia, the loss of skeletal muscle mass and function with aging, is a multifactorial condition that slowly develops over decades and becomes a significant contributor to disability in the older population. Malnutrition and alterations in the muscle anabolic response to nutritional stimuli have been identified as potentially preventable factors that may significantly contribute to sarcopenia. Thus, nutritional interventions may be useful for the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia.
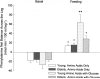
Figures

References
-
- Lamberts SW, van den Beld AW, van der Lely AJ. The endocrinology of aging. Science. 1997;278:419–424. - PubMed
-
- Evans WJ. What is sarcopenia? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1995;50:5–8. Spec No. - PubMed
-
- Morley JE, Baumgartner RN, Roubenoff R, Mayer J, Nair KS. Sarcopenia. J Lab Clin Med. 2001;137:231–243. - PubMed
-
- Roubenoff R, Castaneda C. Sarcopenia-understanding the dynamics of aging muscle. JAMA. 2001;286:1230–1231. - PubMed
-
- Vandervoot AA, Symons TB. Functional and metabolic consequences of sarcopenia. Can J Appl Physiol. 2001;26:90–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
