Epigenetic alteration at the DLK1-GTL2 imprinted domain in human neoplasia: analysis of neuroblastoma, phaeochromocytoma and Wilms' tumour
- PMID: 15798773
- PMCID: PMC2362015
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602478
Epigenetic alteration at the DLK1-GTL2 imprinted domain in human neoplasia: analysis of neuroblastoma, phaeochromocytoma and Wilms' tumour
Abstract
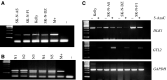
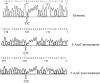
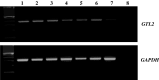
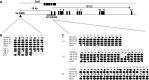
Epigenetic alterations in the 11p15.5 imprinted gene cluster are frequent in human cancers and are associated with disordered imprinting of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)2 and H19. Recently, an imprinted gene cluster at 14q32 has been defined and includes two closely linked but reciprocally imprinted genes, DLK1 and GTL2, that have similarities to IGF2 and H19, respectively. Both GTL2 and H19 are maternally expressed RNAs with no protein product and display paternal allele promoter region methylation, and DLK1 and IGF2 are both paternally expressed. To determine whether methylation alterations within the 14q32 imprinted domain occur in human tumorigenesis, we investigated the status of the GTL2 promoter differentially methylated region (DMR) in 20 neuroblastoma tumours, 20 phaeochromocytomas and, 40 Wilms' tumours. Hypermethylation of the GTL2 promoter DMR was detected in 25% of neuroblastomas, 10% of phaeochromocytoma and 2.5% of Wilms' tumours. Tumours with GTL2 promoter DMR hypermethylation also demonstrated hypermethylation at an upstream intergenic DMR thought to represent a germline imprinting control element. Analysis of neuroblastoma cell lines revealed that GTL2 DMR hypermethylation was associated with transcriptional repression of GTL2. These epigenetic findings are similar to those reported in Wilms' tumours in which H19 repression and DMR hypermethylation is associated with loss of imprinting (LOI, biallelic expression) of IGF2. However, a neuroblastoma cell line with hypermethylation of the GTL2 promoter and intergenic DMR did not show LOI of DLK1 and although treatment with a demethylating agent restored GTL2 expression and reduced DLK1 expression. As described for IGF2/H19, epigenetic changes at DLK1/GTL2 occur in human cancers. However, these changes are not associated with DLK1 LOI highlighting differences in the imprinting control mechanisms operating in the IGF2-H19 and DLK1-GTL2 domains. GTL2 promoter and intergenic DMR hypermethylation is associated with the loss of GTL2 expression and this may contribute to tumorigenesis in a subset of human cancers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imprinting, expression, and localisation of DLK1 in Wilms tumours.J Clin Pathol. 2005 Feb;58(2):145-50. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2004.021717. J Clin Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15677533 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular structure of bovine Gtl2 gene and DNA methylation status of Dlk1-Gtl2 imprinted domain in cloned bovines.Anim Reprod Sci. 2011 Aug;127(1-2):23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Anim Reprod Sci. 2011. PMID: 21820255
-
Altered expression of imprinted genes in Wilms tumors.Oncol Rep. 2011 Mar;25(3):817-23. doi: 10.3892/or.2010.1113. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21174059
-
Role of genomic imprinting in Wilms' tumour and overgrowth disorders.Med Pediatr Oncol. 1996 Nov;27(5):470-5. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-911X(199611)27:5<470::AID-MPO14>3.0.CO;2-E. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1996. PMID: 8827076 Review.
-
Inherited and Sporadic Epimutations at the IGF2-H19 locus in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Wilms' tumor.Endocr Dev. 2009;14:1-9. doi: 10.1159/000207461. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Endocr Dev. 2009. PMID: 19293570 Review.
Cited by
-
Deregulated expression of the imprinted DLK1-DIO3 region in glioblastoma stemlike cells: tumor suppressor role of lncRNA MEG3.Neuro Oncol. 2020 Dec 18;22(12):1771-1784. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa127. Neuro Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32459347 Free PMC article.
-
Maternally expressed gene 3, an imprinted noncoding RNA gene, is associated with meningioma pathogenesis and progression.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 15;70(6):2350-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3885. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20179190 Free PMC article.
-
Shared Copy Number Variation in Simultaneous Nephroblastoma and Neuroblastoma due to Fanconi Anemia.Mol Syndromol. 2012 Sep;3(3):120-130. doi: 10.1159/000341935. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Mol Syndromol. 2012. PMID: 23112754 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA MEG3 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma progression via GATA3.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Jan;13(1):195-208. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13532. Epub 2022 Dec 18. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 36468944 Free PMC article.
-
The Beginning of the Road for Non-Coding RNAs in Normal Hematopoiesis and Hematologic Malignancies.Front Genet. 2011 Dec 28;2:94. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2011.00094. eCollection 2011. Front Genet. 2011. PMID: 22303388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charlier C, Segers K, Karim L, Shay T, Gyapay G, Cockett N, Georges M (2001) The Callipyge mutation enhances the expression of coregulated imprinted genes in cis without affecting their imprinting status. Nat Genet 27: 367–369 - PubMed
-
- Cui H, Niemitz EL, Ravenel JD, Onyango P, Brandenburg SA, Lobanenkov VV, Feinberg AP (2001) Loss of imprinting of insulin-like growth factor-II in Wilms' tumor commonly involves altered methylation but not mutations of CTCF or its binding site. Cancer Res 61: 4947–4950 - PubMed
-
- Feinberg AP, Cui H, Ohlsson R (2002) DNA methylation and genomic imprinting: insights from cancer into epigenetic mechanisms. Semin Cancer Biol 12: 389–398 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

