Intravascular immune surveillance by CXCR6+ NKT cells patrolling liver sinusoids
- PMID: 15799695
- PMCID: PMC1073691
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030113
Intravascular immune surveillance by CXCR6+ NKT cells patrolling liver sinusoids
Abstract
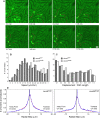
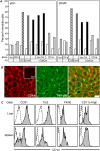
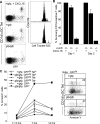
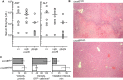
We examined the in vivo behavior of liver natural killer T cells (NKT cells) by intravital fluorescence microscopic imaging of mice in which a green fluorescent protein cDNA was used to replace the gene encoding the chemokine receptor CXCR6. NKT cells, which account for most CXCR6(+) cells in liver, were found to crawl within hepatic sinusoids at 10-20 microm/min and to stop upon T cell antigen receptor activation. CXCR6-deficient mice exhibited a selective and severe reduction of CD1d-reactive NKT cells in the liver and decreased susceptibility to T-cell-dependent hepatitis. CXCL16, the cell surface ligand for CXCR6, is expressed on sinusoidal endothelial cells, and CXCR6 deficiency resulted in reduced survival, but not in altered speed or pattern of patrolling of NKT cells. Thus, NKT cells patrol liver sinusoids to provide intravascular immune surveillance, and CXCR6 contributes to liver-based immune responses by regulating their abundance.
Figures


References
-
- Crispe IN. Hepatic T cells and liver tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:51–62. - PubMed
-
- Manns MP, Strassburg CP. Autoimmune hepatitis: Clinical challenges. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:1502–1517. - PubMed
-
- Lavanchy D. Public health measures in the control of viral hepatitis: A World Health Organization perspective for the next millennium. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17(Suppl):S452–S459. - PubMed
-
- Reiner SL, Locksley RM. The regulation of immunity to Leishmania major . Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:151–177. - PubMed
-
- Baldacci P, Menard R. The elusive malaria sporozoite in the mammalian host. Mol Microbiol. 2004;54:298–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

