Regulatory variation at glypican-3 underlies a major growth QTL in mice
- PMID: 15799711
- PMCID: PMC1073695
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030135
Regulatory variation at glypican-3 underlies a major growth QTL in mice
Abstract
The genetic basis of variation in complex traits remains poorly understood, and few genes underlying variation have been identified. Previous work identified a quantitative trait locus (QTL) responsible for much of the response to selection on growth in mice, effecting a change in body mass of approximately 20%. By fine-mapping, we have resolved the location of this QTL to a 660-kb region containing only two genes of known function, Gpc3 and Gpc4, and two other putative genes of unknown function. There are no non-synonymous polymorphisms in any of these genes, indicating that the QTL affects gene regulation. Mice carrying the high-growth QTL allele have approximately 15% lower Gpc3 mRNA expression in kidney and liver, whereas expression differences at Gpc4 are non-significant. Expression profiles of the two other genes within the region are inconsistent with a factor responsible for a general effect on growth. Polymorphisms in the 3' untranslated region of Gpc3 are strong candidates for the causal sequence variation. Gpc3 loss-of-function mutations in humans and mice cause overgrowth and developmental abnormalities. However, no deleterious side-effects were detected in our mice, indicating that genes involved in Mendelian diseases also contribute to complex trait variation. Furthermore, these findings show that small changes in gene expression can have substantial phenotypic effects.
Figures

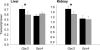

References
-
- Mackay TFC. The genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Annu Rev Genet. 2001;35:303–339. - PubMed
-
- Glazier AM, Nadeau JH, Aitman TJ. Finding genes that underlie complex traits. Science. 2002;298:2345–2349. - PubMed
-
- Olofsson P, Holmberg J, Tordsson J, Lu SM, Akerstrom B, et al. Positional identification of Ncf1 as a gene that regulates arthritis severity in rats. Nat Genet. 2003;33:25–32. - PubMed
-
- Van Laere AS, Nguyen M, Braunschweig M, Nezer C, Collette C, et al. A regulatory mutation in IGF2 causes a major QTL effect on muscle growth in the pig. Nature. 2003;425:832–836. - PubMed
-
- Yalcin B, Willis-Owen SAG, Fullerton J, Meesaq A, Deacon RM, et al. Genetic dissection of a behavioral quantitative trait locus shows that Rgs2 modulates anxiety in mice. Nat Genet. 2004;36:1197–1202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

