Step-response analysis of chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 15800192
- PMCID: PMC6724890
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5133-04.2005
Step-response analysis of chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
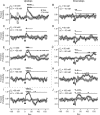
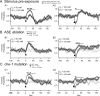
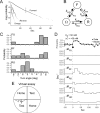
The sensorimotor transformation underlying Caenorhabditis elegans chemotaxis has been difficult to measure directly under normal assay conditions. Thus, key features of this transformation remain obscure, such as its time course and dependence on stimulus amplitude. Here, we present a comprehensive characterization of the transformation as obtained by inducing stepwise temporal changes in attractant concentration within the substrate as the worm crawls across it. We found that the step response is complex, with multiple phases and a nonlinear dependence on the sign and amplitude of the stimulus. Nevertheless, the step response could be reduced to a simple kinetic model that predicted the results of chemotaxis assays. Analysis of the model showed that chemotaxis results from the combined effects of approach and avoidance responses to concentration increases and decreases, respectively. Surprisingly, ablation of the ASE chemosensory neurons, known to be necessary for chemotaxis in chemical gradient assays, eliminated avoidance responses but left approach responses intact. These results indicate that the transformation can be dissected into components to which identified neurons can be assigned.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional asymmetry in Caenorhabditis elegans taste neurons and its computational role in chemotaxis.Nature. 2008 Jul 3;454(7200):114-7. doi: 10.1038/nature06927. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18596810 Free PMC article.
-
The neural network for chemotaxis to tastants in Caenorhabditis elegans is specialized for temporal differentiation.J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 23;29(38):11904-11. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0594-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19776276 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel use of two behavioral mechanisms for chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Neurosci. 2009 Apr 29;29(17):5370-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3633-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19403805 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and modulation of chemosensory behaviors in C. elegans.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Aug;454(5):721-34. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0196-9. Epub 2007 Jan 6. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17206445 Review.
-
Specification of chemosensory neuron subtype identities in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004 Feb;14(1):22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2004.01.006. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15018934 Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding complex behaviors by analyzing optimized models: C. elegans gradient navigation.HFSP J. 2007 Nov;1(4):263-73. doi: 10.2976/1.2786269. Epub 2007 Oct 15. HFSP J. 2007. PMID: 19404426 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic switching system for analyzing chemotaxis responses of wortmannin-inhibited HL-60 cells.Biomed Microdevices. 2008 Aug;10(4):499-507. doi: 10.1007/s10544-007-9158-z. Biomed Microdevices. 2008. PMID: 18205049 Free PMC article.
-
Functional asymmetry in Caenorhabditis elegans taste neurons and its computational role in chemotaxis.Nature. 2008 Jul 3;454(7200):114-7. doi: 10.1038/nature06927. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18596810 Free PMC article.
-
Encoding asymmetry within neural circuits.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Dec;13(12):832-43. doi: 10.1038/nrn3371. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23165260 Review.
-
Microfluidic system for measuring neutrophil migratory responses to fast switches of chemical gradients.Lab Chip. 2006 Feb;6(2):191-8. doi: 10.1039/b511877h. Epub 2005 Dec 23. Lab Chip. 2006. PMID: 16450027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bargmann CI, Horvitz HR (1991) Chemosensory neurons with overlapping functions direct chemotaxis to multiple chemicals in C. elegans Neuron 7: 729-742. - PubMed
-
- Bialek W, Rieke F, de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Warland D (1991) Reading a neural code. Science 252: 1854-1857. - PubMed
-
- Block SM, Segall JE, Berg HC (1982) Impulse responses in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell 31: 215-226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
