Sonic hedgehog has a dual effect on the growth of retinal ganglion axons depending on its concentration
- PMID: 15800198
- PMCID: PMC1564194
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4938-04.2005
Sonic hedgehog has a dual effect on the growth of retinal ganglion axons depending on its concentration
Abstract
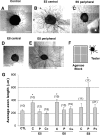
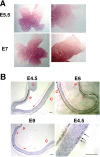
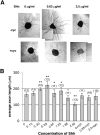
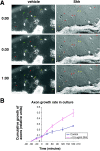
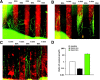
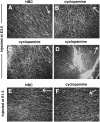
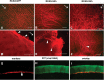
The stereotypical projection of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) axons to the optic disc has served as a good model system for studying axon guidance. By both in vitro and in vivo experiments, we show that a secreted molecule, Sonic hedgehog (Shh), may play a critical role in the process. It is expressed in a dynamic pattern in the ganglion cell layer with a relatively higher expression in the center of the retina. Through gel culture and stripe assays, we show that Shh has a dual effect on RGC axonal growth, acting as a positive factor at low concentrations and a negative factor at high concentrations. Results from time-lapse video microscopic and stripe assay experiments further suggest that the effects of Shh on axons are not likely attributable to indirect transcriptional regulation by Shh. Overexpression of Shh protein or inhibition of Shh function inside the retina resulted in a complete loss of centrally directed projection of RGC axons, suggesting that precise regulation of Shh level inside the retina is critical for the projection of RGC axons to the optic disc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of retinal ganglion cell axon growth: a new role for Sonic hedgehog.Development. 2001 Oct;128(20):3927-36. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.20.3927. Development. 2001. PMID: 11641217
-
Sonic hedgehog is indirectly required for intraretinal axon pathfinding by regulating chemokine expression in the optic stalk.Development. 2012 Jul;139(14):2604-13. doi: 10.1242/dev.077594. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Development. 2012. PMID: 22696293 Free PMC article.
-
Negative guidance factor-induced macropinocytosis in the growth cone plays a critical role in repulsive axon turning.J Neurosci. 2009 Aug 26;29(34):10488-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2355-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19710302 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglion cell axon pathfinding in the retina and optic nerve.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Feb;15(1):125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.09.006. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15036215 Review.
-
Intraretinal projection of retinal ganglion cell axons as a model system for studying axon navigation.Brain Res. 2008 Feb 4;1192:165-77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.116. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 17320832 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;14(7):416-29. doi: 10.1038/nrm3598. Epub 2013 May 30. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23719536 Review.
-
Large-scale microfluidic gradient arrays reveal axon guidance behaviors in hippocampal neurons.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2017 May 8;3:17003. doi: 10.1038/micronano.2017.3. eCollection 2017. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2017. PMID: 31057858 Free PMC article.
-
Pathfinding in a large vertebrate axon tract: isotypic interactions guide retinotectal axons at multiple choice points.Development. 2008 Sep;135(17):2865-71. doi: 10.1242/dev.025049. Epub 2008 Jul 24. Development. 2008. PMID: 18653554 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant Hedgehog ligands induce progressive pancreatic fibrosis by paracrine activation of myofibroblasts and ductular cells in transgenic zebrafish.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e27941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027941. Epub 2011 Dec 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22164219 Free PMC article.
-
Segregation of ipsilateral retinal ganglion cell axons at the optic chiasm requires the Shh receptor Boc.J Neurosci. 2010 Jan 6;30(1):266-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3778-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20053908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augsburger A, Schuchardt A, Hoskins S, Dodd J, Butler S (1999) BMPs as mediators of roof plate repulsion of commissural neurons. Neuron 24: 127-141. - PubMed
-
- Bao ZZ, Bruneau BG, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Cepko CL (1999) Regulation of chamber-specific gene expression in the developing heart by Irx4. Science 283: 1161-1164. - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Taipale J, Olson JM, Beachy PA (2002) Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 297: 1559-1561. - PubMed
-
- Birgbauer E, Cowan CA, Sretavan DW, Henkemeyer M (2000) Kinase independent function of EphB receptors in retinal axon pathfinding to the optic disc from dorsal but not ventral retina. Development [Suppl] 127: 1231-1241. - PubMed
-
- Brittis PA, Lemmon V, Rutishauser U, Silver J (1995) Unique changes of ganglion cell growth cone behavior following cell adhesion molecule perturbations: a time-lapse study of the living retina. Mol Cell Neurosci 6: 433-449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
