Structural basis for 5'-end-specific recognition of guide RNA by the A. fulgidus Piwi protein
- PMID: 15800629
- PMCID: PMC4694588
- DOI: 10.1038/nature03514
Structural basis for 5'-end-specific recognition of guide RNA by the A. fulgidus Piwi protein
Abstract
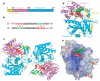
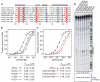
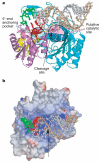
RNA interference (RNAi) is a conserved sequence-specific gene regulatory mechanism mediated by the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is composed of a single-stranded guide RNA and an Argonaute protein. The PIWI domain, a highly conserved motif within Argonaute, has been shown to adopt an RNase H fold critical for the endonuclease cleavage activity of RISC. Here we report the crystal structure of Archaeoglobus fulgidus Piwi protein bound to double-stranded RNA, thereby identifying the binding pocket for guide-strand 5'-end recognition and providing insight into guide-strand-mediated messenger RNA target recognition. The phosphorylated 5' end of the guide RNA is anchored within a highly conserved basic pocket, supplemented by the carboxy-terminal carboxylate and a bound divalent cation. The first nucleotide from the 5' end of the guide RNA is unpaired and stacks over a conserved tyrosine residue, whereas successive nucleotides form a four-base-pair RNA duplex. Mutation of the corresponding amino acids that contact the 5' phosphate in human Ago2 resulted in attenuated mRNA cleavage activity. Our structure of the Piwi-RNA complex, and that determined elsewhere, provide direct support for the 5' region of the guide RNA serving as a nucleation site for pairing with target mRNA and for a fixed distance separating the RISC-mediated mRNA cleavage site from the anchored 5' end of the guide RNA.
Figures
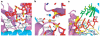
Similar articles
-
Structural insights into mRNA recognition from a PIWI domain-siRNA guide complex.Nature. 2005 Mar 31;434(7033):663-6. doi: 10.1038/nature03462. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15800628 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of A. aeolicus argonaute, a site-specific DNA-guided endoribonuclease, provides insights into RISC-mediated mRNA cleavage.Mol Cell. 2005 Aug 5;19(3):405-19. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.07.011. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16061186 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a PIWI protein suggests mechanisms for siRNA recognition and slicer activity.EMBO J. 2004 Dec 8;23(24):4727-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600488. Epub 2004 Nov 25. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15565169 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of target RNA transcript recognition by Argonaute-guide complexes.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:45-50. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.029. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381279 Review.
-
Structural biology of RNA silencing and its functional implications.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:81-93. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.053. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prokaryotic Argonaute Proteins as a Tool for Biotechnology.Mol Biol. 2022;56(6):854-873. doi: 10.1134/S0026893322060103. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36060308 Free PMC article.
-
CBX4-mediated SUMO modification regulates BMI1 recruitment at sites of DNA damage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(12):5497-510. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks222. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22402492 Free PMC article.
-
Importin-β facilitates nuclear import of human GW proteins and balances cytoplasmic gene silencing protein levels.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 3;43(15):7447-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv705. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26170235 Free PMC article.
-
Essential notes regarding the design of functional siRNAs for efficient mammalian RNAi.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006;2006(4):65052. doi: 10.1155/JBB/2006/65052. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17057367 Free PMC article.
-
Six RNA viruses and forty-one hosts: viral small RNAs and modulation of small RNA repertoires in vertebrate and invertebrate systems.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Feb 12;6(2):e1000764. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000764. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20169186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hutvagner G, Zamore PD. RNAi: nature abhors a double-strand. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002;12:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Hannon GJ. RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418:244–251. - PubMed
-
- Meister G, Tuschl T. Mechanism of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature. 2004;431:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Song JJ, Smith SK, Hannon GJ, Joshua-Tor L. Crystal structure of Argonaute and its implications for RISC slicer activity. Science. 2004;305:1434–1437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

