Relationship between serum b2-microglobulin levels and virological breakthrough in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients, under long-term treatment schedules including lamivudine
- PMID: 15800981
- PMCID: PMC4305712
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i13.1922
Relationship between serum b2-microglobulin levels and virological breakthrough in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients, under long-term treatment schedules including lamivudine
Abstract
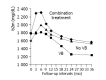
Aim: Predictive value of serum b2-microglobulin (b2m) levels for virological breakthrough (VB) in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients under long-term treatment schedules including lamivudine (LAM).
Methods: Serum b2m levels were calculated during treatment in 25 CHB patients under long-term LAM monotherapy (group A) and 12 patients under initial interferon plus LAM treatment followed by LAM monotherapy (group B), using the MEIA technology. We used Cox proportional hazard models in order to investigate the association between serum b2m levels and VB.
Results: Seven of 25 patients (28%), 9/25 (36%) and 14/25 (56%) from group A and 0/12, 2/12 (16.6%) and 3/12 (25%) from group B exhibited VB at months 12, 24 and 36 of treatment, respectively. All patients, from both groups, who did not show VB exhibited b2m elevation in mo 3. The duration of b2m elevation was significantly longer in the virological responder's subgroup from group A than the non-responder's one (7.3+/-2.6 vs 3.8+/-3.4 mo, P = 0.02). In comparison to group A patients whose b2m levels were increased at 3 mo, patients whose b2m levels were decreased had 4.6 times higher risk of experiencing VB (RR = 4.6, P = 0.024). When baseline variables were simultaneously included in the same Cox model, decreased b2m status was still associated with increased risk of VB (RR = 12.2, P = 0.03).
Conclusion: In HBeAg-negative CHB patients under either long-term LAM monotherapy or initial combination treatment, serum b2m levels at 3 mo of treatment, compared to baseline ones, might be a predictor of risk for VB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum beta2-microglobulin levels in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients under long term lamivudine monotherapy: relationship with virological breakthrough.Can J Gastroenterol. 2004 May;18(5):307-13. doi: 10.1155/2004/864292. Can J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15152280
-
Adefovir plus lamivudine are more effective than adefovir alone in lamivudine-resistant HBeAg- chronic hepatitis B patients: a 4-year study.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Jan;25(1):54-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05952.x. Epub 2009 Sep 22. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 19780875 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical significance of hepatitis B e antigen level measurement during long-term lamivudine therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients with e antigen positive.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Nov 7;12(41):6693-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i41.6693. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17075986 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy for up to 5 years in lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B.Antivir Ther. 2010;15(2):235-41. doi: 10.3851/IMP1510. Antivir Ther. 2010. PMID: 20386079 Clinical Trial.
-
Lamivudine monotherapy and lamivudine plus interferon alpha combination therapy in HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B not responding to previous interferon alpha monotherapy.Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2007 Jan-Mar;70(1):20-4. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2007. PMID: 17619534 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Monoclonal antibodies directed against chicken β2-microglobulin developed with a synthesized peptide.Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2013 Jun;32(3):205-10. doi: 10.1089/mab.2013.0001. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23750479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The World Health Report. WHO 1998
-
- Schalm SW, Thomas HC, Hadziyannis SJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Prog Liver Dis. 1990;9:443–462. - PubMed
-
- Carman WF, Jacyna MR, Hadziyannis S, Karayiannis P, McGarvey MJ, Makris A, Thomas HC. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1989;2:588–591. - PubMed
-
- Laras A, Koskinas J, Avgidis K, Hadziyannis SJ. Incidence and clinical significance of hepatitis B virus precore gene translation initiation mutations in e antigen-negative patients. J Viral Hepat. 1998;5:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Brunetto MR, Giarin M, Saracco G, Oliveri F, Calvo P, Capra G, Randone A, Abate ML, Manzini P, Capalbo M. Hepatitis B virus unable to secrete e antigen and response to interferon in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:845–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

