Therapeutic innovation in the European Union: analysis of the drugs approved by the EMEA between 1995 and 2003
- PMID: 15801943
- PMCID: PMC1884813
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02320.x
Therapeutic innovation in the European Union: analysis of the drugs approved by the EMEA between 1995 and 2003
Abstract
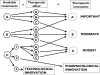
Since January 1995, all European Union applications for marketing approval for medicinal products derived from biotechnology and other drugs considered potentially innovative follow the EMEA centralized procedure. In order to assess the overall degree of therapeutic innovation of these drugs, we considered, for each approved agent, its target, the availability of previous treatments and the extent of its therapeutic effect. The following scores for therapeutic innovation were assigned through a consensus process: 'A' (important), 'B' (moderate) and 'C' (modest). The overall degree of important/moderate therapeutic innovation was 47% of all therapeutic agents (32% important; 15% moderate). Most (80%) of the EMEA-approved therapeutic agents were for serious diseases. The remaining ones were for risk factors (7%) or nonserious diseases (13%).
Figures
Comment in
-
Drug development: more science, more education.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Apr;59(4):377-8. doi: 10.1111/j.0306-5251.2005.02420.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15801930 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
On criteria to evaluate the therapeutic innovation of drugs.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 May;87(5):2403-2404. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14650. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33219565 No abstract available.
References
-
- Garattini S, Bertele' V. Efficacy, safety and cost of new drugs acting on the central nervous system. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;59:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Garattini S, Bertele' V. Efficacy, safety and cost of new cardiovascular drugs: a survey. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;59:701–6. - PubMed
-
- International Society of Drugs Bulletins declaration. 2001. http://www.isdbweb.org/
-
- EMEA 2003 European Public Assessment Reports. http://www.emea.eu.int/index/indexh1.htm.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

