Epidermal growth factor mediates detachment from and invasion through collagen I and Matrigel in Capan-1 pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 15801978
- PMCID: PMC1079814
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-5-12
Epidermal growth factor mediates detachment from and invasion through collagen I and Matrigel in Capan-1 pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is a highly invasive neoplasm. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its receptor are over expressed in pancreatic cancer, and expression correlates with invasion and metastasis. We hypothesized that EGF receptor and integrin signalling pathways interact in mediating cellular adhesion and invasion in pancreatic cancer, and that invasiveness correlates temporally with detachment from extracellular matrix.
Methods: We tested this hypothesis by investigating the role of EGF in mediating adhesion to and invasion through collagen I and Matrigel in the metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line Capan-1. Adhesion and invasion were measured using in vitro assays of fluorescently-labeled cells. Adhesion and invasion assays were also performed in the primary pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line MIA PaCa-2.
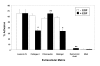
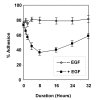
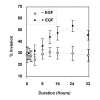
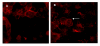
Results: EGF inhibited adhesion to collagen I and Matrigel in Capan-1 cells. The loss of adhesion was reversed by AG825, an inhibitor of erbB2 receptor signalling and by wortmannin, a PI3K inhibitor, but not by the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide. EGF stimulated invasion through collagen I and Matrigel at concentrations and time courses similar to those mediating detachment from these extracellular matrix components. Adhesion to collagen I was different in MIA PaCa-2 cells, with no significant change elicited following EGF treatment, whereas treatment with the EGF family member heregulin-alpha elicited a marked increase in adhesion. Invasion through Matrigel in response to EGF, however, was similar to that observed in Capan-1 cells.
Conclusion: An inverse relationship exists between adhesion and invasion capabilities in Capan-1 cells but not in MIA PaCa-2 cells. EGF receptor signalling involving the erbB2 and PI3K pathways plays a role in mediating these events in Capan-1 cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor modulates prostate cancer cell invasiveness regulating urokinase-type plasminogen activator activity. EGF-receptor inhibition may prevent tumor cell dissemination.Thromb Haemost. 2005 May;93(5):964-75. doi: 10.1160/TH04-09-0637. Thromb Haemost. 2005. PMID: 15886816
-
Cytokines modulate MIA PaCa 2 and CAPAN-1 adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins.Pancreas. 1999 Nov;19(4):362-9. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199911000-00007. Pancreas. 1999. PMID: 10547196
-
Effects of epidermal growth factor on invasiveness through the extracellular matrix in high- and low-metastatic clones of RCT sarcoma in vitro.Jpn J Cancer Res. 1994 Jan;85(1):63-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1994.tb02887.x. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1994. PMID: 8106290 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer metastases: challenges and opportunities.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Sep;5(5):402-18. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of collagenase IV and cell adhesion reduce the invasive activity of malignant tumour cells.Ciba Found Symp. 1988;141:193-210. doi: 10.1002/9780470513736.ch11. Ciba Found Symp. 1988. PMID: 2855414 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Cell Cultures for MRI Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 3;23(17):10109. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710109. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into erlotinib action in pancreatic cancer cells using a combined experimental and mathematical approach.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Nov 21;18(43):6226-34. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6226. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23180942 Free PMC article.
-
Occult polyclonality of preclinical pancreatic cancer models drives in vitro evolution.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 25;13(1):3652. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31376-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35752636 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotype and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines.Pancreas. 2010 May;39(4):425-35. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181c15963. Pancreas. 2010. PMID: 20418756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The small heat shock protein αA-crystallin negatively regulates pancreatic tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):65808-65824. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11668. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27588467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y, Pan G, Hou X, Liu T, Chen J, Yanaihara C, Yanaihara N. Epidermal growth factor and its receptors in human pancreatic carcinoma. Pancreas. 1990;5:278–283. - PubMed
-
- Korc M, Chandrasekar B, Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Buchler M, Beger H. Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human pancreatic cancer is associated with concomitant increases in the levels of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:1352–1360. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Kobrin M, Buchler M, Beger H, Korc M. Coexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor and ligands in human pancreatic cancer is associated with enhanced tumor aggressiveness. Anticancer Res. 1993;13:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Ohlsson B, Jansen C, Ihse I, Axelson J. Epidermal growth factor induces cell proliferation in mouse pancreas and salivary glands. Pancreas. 1997;14:94–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

