Resveratrol and estradiol exert disparate effects on cell migration, cell surface actin structures, and focal adhesion assembly in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 15802018
- PMCID: PMC1501122
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04346
Resveratrol and estradiol exert disparate effects on cell migration, cell surface actin structures, and focal adhesion assembly in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells
Abstract
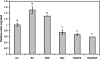
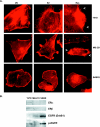
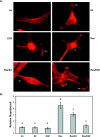
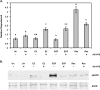
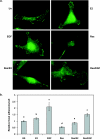
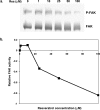
Resveratrol, a grape polyphenol, is thought to be a cancer preventive, yet its effects on metastatic breast cancer are relatively unknown. Since cancer cell invasion is dependent on cell migration, the chemotactic response of MDA-MB-231 metastatic human breast cancer cells to resveratrol, estradiol (E2), or epidermal growth factor (EGF) was investigated. Resveratrol decreased while E2 and EGF increased directed cell migration. Resveratrol may inhibit cell migration by altering the cytoskeleton. Resveratrol induced a rapid global array of filopodia and decreased focal adhesions and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity. E2 or EGF treatment did not affect filopodia extension but increased lamellipodia and associated focal adhesions that are integral for cell migration. Combined resveratrol and E2 treatment resulted in a filopodia and focal adhesion response similar to resveratrol alone. Combined resveratrol and EGF resulted in a lamellipodia and focal adhesion response similar to EGF alone. E2 and to a lesser extent resveratrol increased EGFR activity. The cytoskeletal changes and EGFR activity in response to E2 were blocked by EGFR1 inhibitor indicating that E2 may increase cell migration via crosstalk with EGFR signaling. These data suggest a promotional role for E2 in breast cancer cell migration but an antiestrogenic, preventative role for resveratrol.
Figures
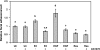
Similar articles
-
Estrogen and resveratrol regulate Rac and Cdc42 signaling to the actin cytoskeleton of metastatic breast cancer cells.Neoplasia. 2007 Feb;9(2):147-58. doi: 10.1593/neo.06778. Neoplasia. 2007. PMID: 17356711 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoid effects relevant to cancer.J Nutr. 2002 Nov;132(11 Suppl):3482S-3489S. doi: 10.1093/jn/132.11.3482S. J Nutr. 2002. PMID: 12421874
-
Adhesion, actin cytoskeleton organisation and the spreading of colon adenocarcinoma cells induced by EGF are mediated by alpha2beta1 integrin low clustering through focal adhesion kinase.Histochem Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;116(4):337-48. doi: 10.1007/s004180100324. Histochem Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11702192
-
Targeting vascular cell migration as a strategy for blocking angiogenesis: the central role of focal adhesion protein tyrosine kinase family.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(21):2129-45. doi: 10.2174/138161207781039643. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17627545 Review.
-
Mechanical integration of actin and adhesion dynamics in cell migration.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:315-33. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.011209.122036. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19575647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol induces long-lasting IL-8 expression and peculiar EGFR activation/distribution in human keratinocytes: mechanisms and implications for skin administration.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059632. Epub 2013 Mar 18. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527233 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled receptor 30 in tumor development.Endocrine. 2010 Aug;38(1):29-37. doi: 10.1007/s12020-010-9363-z. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Endocrine. 2010. PMID: 20960099 Review.
-
Steroid Receptor Signallings as Targets for Resveratrol Actions in Breast and Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 3;20(5):1087. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051087. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30832393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of mammary tumor growth and metastases to bone and liver by dietary grape polyphenols.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26(6):505-16. doi: 10.1007/s10585-009-9250-2. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009. PMID: 19294520 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary grape polyphenol resveratrol increases mammary tumor growth and metastasis in immunocompromised mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Jan 8;13:6. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-6. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 23298290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McDonnell DP, Norris JD. Connections and regulation of the human estrogen receptor. Science. 2002;296:1642–1644. - PubMed
-
- Cavalieri EL, Rogan EG. A unified mechanism in the initiation of cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;959:341–354. - PubMed
-
- Salih AK, Fentiman IS. Breast cancer prevention: present and future. Cancer Treat Rev. 2001;27:261–273. - PubMed
-
- Shen Q, Brown PH. Novel agents for the prevention of breast cancer: targeting transcription factors and signal transduction pathways. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003;8:45–73. - PubMed
-
- Katzenellenbogen BS, Choi I, Delage-Mourroux R, Ediger TR, Martini PG, Montano M, Sun J, Weis K, Katzenellenbogen JA. Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: selective ligands and receptor pharmacology. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2000;74:279–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
