Therapeutic efficacy of adenoviral-mediated p53 gene transfer is synergistically enhanced by combined use of antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeting clusterin gene in a human bladder cancer model
- PMID: 15802022
- PMCID: PMC1501130
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04478
Therapeutic efficacy of adenoviral-mediated p53 gene transfer is synergistically enhanced by combined use of antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeting clusterin gene in a human bladder cancer model
Abstract
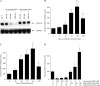
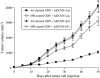
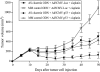
To establish a more effective therapeutic strategy against advanced bladder cancer, we investigated the effects of combined treatment with antisense (AS) oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) targeting the anti-apoptotic gene clusterin and adenoviral-mediated p53 gene transfer (Ad5CMV-p53) using the human bladder cancer KoTCC-1 model. Clusterin expression in KoTCC-1 cells was highly upregulated by Ad5CMV-p53 treatment; however, AS clusterin ODN treatment further suppressed clusterin expression in KoTCC-1 cells after Ad5CMV-p53 treatment. AS clusterin ODN treatment synergistically enhanced the cytotoxic effect of Ad5CMV-p53, and DNA fragmentation characteristic of apoptosis was observed only after combined treatment with AS clusterin ODN and Ad5CMV-p53, but not after treatment with either agent alone. Administration of AS clusterin ODN and Ad5CMV-p53 into nude mice resulted in a significant inhibition of KoTCC-1 tumor growth as well as lymph node metastases compared to administration of either agent alone. Furthermore, combined treatment with AS clusterin ODN, Ad5CMV-p53, and cisplatin completely eradicated KoTCC-1 tumors and lymph node metastases in 60% and 100% of mice, respectively. These findings suggest that combined treatment with AS clusterin ODN and Ad5CMV-p53 could be a novel strategy to inhibit bladder cancer progression, and that further additional use of a chemotherapeutic agent may substantially enhance the efficacy of this combined regimen.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic chemsensitization and inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis by the antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeting clusterin gene in a human bladder cancer model.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Dec;7(12):4245-52. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11751526
-
Synergistic antitumor effect of combined use of adenoviral-mediated p53 gene transfer and antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeting clusterin gene in an androgen-independent human prostate cancer model.Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 Feb;4(2):187-95. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005. PMID: 15713890
-
Enhanced radiosensitivity by inhibition of the anti-apoptotic gene clusterin using antisense oligodeoxynucleotide in a human bladder cancer model.Oncol Rep. 2005 May;13(5):885-90. Oncol Rep. 2005. PMID: 15809754
-
Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide therapy targeting clusterin gene for prostate cancer: Vancouver experience from discovery to clinic.Int J Urol. 2005 Sep;12(9):785-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2005.01173.x. Int J Urol. 2005. PMID: 16201973 Review.
-
Gene therapy for bladder cancer.World J Urol. 2000 Apr;18(2):148-51. doi: 10.1007/s003450050188. World J Urol. 2000. PMID: 10854151 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth inhibition and enhanced chemosensitivity induced by down-regulation of Aurora-A in human renal cell carcinoma Caki-2 cells using short hairpin RNA.Oncol Lett. 2011 Jul;2(4):713-717. doi: 10.3892/ol.2011.295. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Oncol Lett. 2011. PMID: 22848254 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Targeting Clusterin Using OGX-011 on Antitumor Activity of Temsirolimus in a Human Renal Cell Carcinoma Model.Target Oncol. 2017 Feb;12(1):69-79. doi: 10.1007/s11523-016-0448-3. Target Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27526062
-
Clusterin inhibition using OGX-011 synergistically enhances antitumour activity of sorafenib in a human renal cell carcinoma model.Br J Cancer. 2012 Jun 5;106(12):1945-52. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.209. Epub 2012 May 15. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22588555 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Sensitivity to NVP-BEZ235 by Inhibition of p62/SQSTM1 in Human Bladder Cancer KoTCC-1 Cells Both In Vitro and In Vivo.In Vivo. 2020 May-Jun;34(3):1001-1008. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11868. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32354885 Free PMC article.
-
[The use of p53 as a tool for human cancer therapy].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007 Nov-Dec;41(6):947-63. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007. PMID: 18318112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thurman SA, DeWeese TL. Multimodality therapy for the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Semin Urol Oncol. 2000;18:313–322. - PubMed
-
- Vaughn DJ, Malkowicz SB. Recent advances in bladder cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Invest. 2001;19:77–85. - PubMed
-
- Haviv DJ, Curiel DT. Conditional gene targeting for cancer gene therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;53:135–154. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz J. Adenovirus-mediated p53 gene therapy: overview of preclinical studies and potential clinical applications. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 1999;1:500–1509. - PubMed
-
- Spitz FR, Nguyen D, Skibber JM, Meyn RE, Cristiano RJ, Roth JA. Adenoviral-mediated wild-type p53 gene expression sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to ionizing radiation. Clin Cancer Res. 1996;2:1665–1671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
