Immune modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during viral infection
- PMID: 15802953
- PMCID: PMC1224723
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.41
Immune modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during viral infection
Abstract
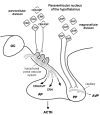
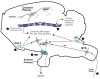
Compelling data has been amassed indicating that soluble factors, or cytokines, emanating from the immune system can have profound effects on the neuroendocrine system, in particular the hypothalamic- pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. HPA activation by cytokines (via the release of glucocorticoids), in turn, has been found to play a critical role in restraining and shaping immune responses. Thus, cytokine-HPA interactions represent a fundamental consideration regarding the maintenance of homeostasis and the development of disease during viral infection. Although reviews exist that focus on the bi-directional communication between the immune system and the HPA axis during viral infection (188,235), others have focused on the immunomodulatory effects of glucocorticoids during viral infection (14,225). This review, however, concentrates on the other side of the bi-directional loop of neuroendocrine-immune interactions, namely, the characterization of HPA axis activity during viral infection and the mechanisms employed by cytokines to stimulate glucocorticoid release.
Figures




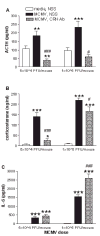
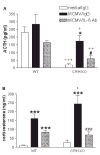

References
-
- Abbas, A.K., and A.H. Lichtman. 1997. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. Elsevier Science, Philadelphia.
-
- Adcock IM, Brown CR, Barnes PJ. Tumour necrosis factor alpha causes retention of activated glucocorticoid receptor within the cytoplasm of A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;225:545–550. - PubMed
-
- Adcock IM, Caramori G. Cross-talk between pro-inflammatory transcription factors and glucocorticoids. Immunol Cell Biol. 2001;79:376–384. - PubMed
-
- Allan W, Tabi Z, Cleary A, et al. Cellular events in the lymph node and lung of mice with influenza. Consequences of depleting CD4+ T cells J Immunol. 1990;144:3980–3986. - PubMed
-
- Amici C, Belardo G, Rossi A, et al. Activation of I kappa b kinase by herpes simplex virus type 1. A novel target for anti-herpetic therapy. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28759–28766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

