Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of a depot formulation of naltrexone in alcoholics: an open-label trial
- PMID: 15804355
- PMCID: PMC1087493
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-5-18
Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of a depot formulation of naltrexone in alcoholics: an open-label trial
Abstract
Background: Naltrexone is an effective medication for treatment of alcohol dependence, but its efficacy is limited by lack of adherence to the oral dosage form. A long-acting depot formulation of naltrexone may increase adherence.
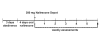
Methods: A single site, 6-week open label study was conducted with 16 alcohol dependent subjects each receiving 300 mg of Naltrexone Depot by intramuscular injection. The main outcomes were safety and tolerability of the Naltrexone Depot formulation, blood levels of naltrexone and its main metabolite 6-beta naltrexol, and self-reported alcohol use. All subjects received weekly individual counseling sessions.
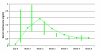
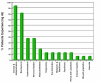
Results: The medication was well tolerated with 88% of subjects completing the 6-week trial. The most common side effect experienced was injection site complications. There were no serious adverse events. Subjects had naltrexone and 6-beta-naltrexol concentrations throughout the trial with mean values ranging from 0.58 ng/mL to 2.04 ng/mL and 1.51 ng/mL to 5.52 ng/mL, respectively, at each sampling time following administration. Compared to baseline, subjects had significantly reduced number of drinks per day, heavy drinking days and proportion of drinking days.
Conclusion: Naltrexone Depot is safe and well tolerated in alcoholics and these findings support the further investigation of its utility in larger double-blind placebo controlled trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of long-acting injectable naltrexone.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006 Mar;30(3):480-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00052.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006. PMID: 16499489 Clinical Trial.
-
The status of naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence: specific effects on heavy drinking.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006 Dec;26(6):610-25. doi: 10.1097/01.jcp.0000245566.52401.20. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17110818 Review.
-
An open clinical trial of naltrexone for amphetamine dependence: compliance and tolerability.Nord J Psychiatry. 2005;59(3):167-71. doi: 10.1080/08039480510023052. Nord J Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 16195116 Clinical Trial.
-
Naltrexone and cue exposure with coping and communication skills training for alcoholics: treatment process and 1-year outcomes.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001 Nov;25(11):1634-47. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001. PMID: 11707638 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-acting injectable naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol dependence.Expert Rev Neurother. 2007 Oct;7(10):1265-77. doi: 10.1586/14737175.7.10.1265. Expert Rev Neurother. 2007. PMID: 17939765 Review.
Cited by
-
The Utilization of Low Dose Naltrexone for Chronic Pain.CNS Drugs. 2023 Aug;37(8):663-670. doi: 10.1007/s40263-023-01018-3. Epub 2023 Jul 28. CNS Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37505425
-
Pharmacological enhancement of naltrexone treatment for opioid dependence: a review.Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2011 Jun;2011(2):113-123. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S15853. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2011. PMID: 21731898 Free PMC article.
-
Improving clinical outcomes for naltrexone as a management of problem alcohol use.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;76(5):632-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04452.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22946873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on neuropharmacological treatments for alcoholism: scientific basis and clinical findings.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Jan 1;75(1):34-56. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.08.005. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17880925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naltrexone depot formulations for opioid and alcohol dependence: a systematic review.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2011 Dec;17(6):629-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00194.x. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2011. PMID: 21554565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Malley SS, Jaffe AJ, Chang G, Schottenfeld RS, Meyer RE, Rounsville B. Naltrexone and coping skills therapy for alcohol dependence: a controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992;49:881–887. - PubMed
-
- Volpicelli JR, Alterman AI, Hayashida M, O'Brien CP. Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992;49:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Balldin J, Berglund M, Borg S, Mansson M, Bendtsen P, Franck J, Gustafsson L, Halldin J, Nilsson LH, Stolt G, Willander A. A 6-month controlled naltrexone study: combined effect with cognitive behavioral therapy in outpatient treatment of alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:1142–1149. doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000075548.83053.A9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anton RF, Moak DH, Waid LR, Latham PK, Malcolm RJ, Dias JK. Naltrexone and cognitive behavioral therapy for the treatment of outpatient alcoholics: results of a placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156:1758–1764. - PubMed
-
- Kranzler HR, Modesto-Lowe V, Nuwayser ES. Sustained-release naltrexone for alcoholism treatment: a preliminary study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:1074–1079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical