The Bacillus subtilis SinR and RapA developmental regulators are responsible for inhibition of spore development by alcohol
- PMID: 15805512
- PMCID: PMC1070374
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.8.2662-2672.2005
The Bacillus subtilis SinR and RapA developmental regulators are responsible for inhibition of spore development by alcohol
Abstract
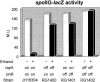
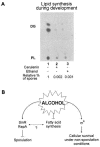
Even though there is a large body of information concerning the harmful effects of alcohol on different organisms, the mechanism(s) that affects developmental programs, at a single-cell level, has not been clearly identified. In this respect, the spore-forming bacterium Bacillus subtilis constitutes an excellent model to study universal questions of cell fate, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis. Here, we demonstrate that treatment with subinhibitory concentrations of alcohol that did not affect vegetative growth inhibited the initiation of spore development through a selective blockage of key developmental genes under the control of the master transcription factor Spo0A approximately P. Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside-directed expression of a phosphorylation-independent form of Spo0A (Sad67) and the use of an in vivo mini-Tn10 insertional library permitted the identification of the developmental SinR repressor and RapA phosphatase as the effectors that mediated the inhibitory effect of alcohol on spore morphogenesis. A double rapA sinR mutant strain was completely resistant to the inhibitory effects of different-C-length alcohols on sporulation, indicating that the two cell fate determinants were the main or unique regulators responsible for the spo0 phenotype of wild-type cells in the presence of alcohol. Furthermore, treatment with alcohol produced a significant induction of rapA and sinR, while the stationary-phase induction of sinI, which codes for a SinR inhibitor, was completely turned off by alcohol. As a result, a dramatic repression of spo0A and the genes under its control occurred soon after alcohol addition, inhibiting the onset of sporulation and permitting the evaluation of alternative pathways required for cellular survival.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of phosphorelay perturbations on architecture, sporulation, and spore resistance in biofilms of Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2006 Apr;188(8):3099-109. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.8.3099-3109.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16585769 Free PMC article.
-
Hpr (ScoC) and the phosphorelay couple cell cycle and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004 Feb 9;231(1):99-110. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00936-4. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004. PMID: 14769473
-
An evolutionary link between sporulation and prophage induction in the structure of a repressor:anti-repressor complex.J Mol Biol. 1998 Nov 13;283(5):907-12. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2163. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9799632 Review.
-
Targets of the master regulator of biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Feb;59(4):1216-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.05019.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16430695
-
Sporulation of Bacillus subtilis.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004 Dec;7(6):579-86. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.001. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15556029 Review.
Cited by
-
A Duo of Potassium-Responsive Histidine Kinases Govern the Multicellular Destiny of Bacillus subtilis.mBio. 2015 Jul 7;6(4):e00581. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00581-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26152584 Free PMC article.
-
A LuxS-dependent cell-to-cell language regulates social behavior and development in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jun;188(12):4442-52. doi: 10.1128/JB.00165-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16740951 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of phosphorelay perturbations on architecture, sporulation, and spore resistance in biofilms of Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2006 Apr;188(8):3099-109. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.8.3099-3109.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16585769 Free PMC article.
-
Very low ethanol concentrations affect the viability and growth recovery in post-stationary-phase Staphylococcus aureus populations.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Apr;72(4):2627-36. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2627-2636.2006. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597967 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis biofilm extends Caenorhabditis elegans longevity through downregulation of the insulin-like signalling pathway.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 30;8:14332. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14332. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28134244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arabolaza, A. L., A. Nakamura, M. E. Pedrido, L. Martelotto, L. Orsaria, and R. Grau. 2003. Characterization of a novel inhibitory feedback of the anti-anti-sigma SpoIIAA on Spo0A activation during development in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 47:1251-1263. - PubMed
-
- Bai, U., I. Mandic-Mulet, and I. Smith. 1993. SinI modulates the activity of SinR, a developmental switch protein of Bacillus subtilis, by protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 7:139-148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

