Catabolite repression of the propionate catabolic genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica: evidence for involvement of the cyclic AMP receptor protein
- PMID: 15805526
- PMCID: PMC1070369
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.8.2793-2800.2005
Catabolite repression of the propionate catabolic genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica: evidence for involvement of the cyclic AMP receptor protein
Abstract
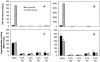
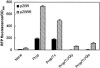
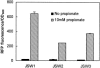
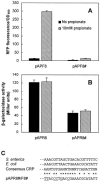
Previous studies with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2 demonstrated that transcriptional activation of the prpBCDE operon requires the function of transcription factor PrpR, sigma-54, and IHF. In this study, we found that transcription from the prpBCDE and prpR promoters was down-regulated by the addition of glucose or glycerol, indicating that these genes may be regulated by the cyclic AMP (cAMP)-cAMP receptor protein (CRP) complex. Targeted mutagenesis of a putative CRP-binding site in the promoter region between prpR and prpBCDE suggested that these genes are under the control of CRP. Furthermore, cells with defects in cya or crp exhibited reduced transcriptional activation of prpR and prpBCDE in Escherichia coli. These results demonstrate that propionate metabolism is subject to catabolite repression by the global transcriptional regulator CRP and that this regulation is effected through control of both the regulator gene prpR and the prpBCDE operon itself. The unique properties of the regulation of these two divergent promoters may have important implications for mechanisms of CRP-dependent catabolite repression acting in conjunction with a member of the sigma-54 family of transcriptional activators.
Figures


Similar articles
-
prpR, ntrA, and ihf functions are required for expression of the prpBCDE operon, encoding enzymes that catabolize propionate in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium LT2.J Bacteriol. 2000 Feb;182(4):905-10. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.4.905-910.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10648513 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of sugar-mediated catabolite repression of the propionate catabolic genes in Escherichia coli.Gene. 2012 Aug 1;504(1):116-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.04.074. Epub 2012 May 3. Gene. 2012. PMID: 22579471
-
2-Methylcitrate-dependent activation of the propionate catabolic operon (prpBCDE) of Salmonella enterica by the PrpR protein.Microbiology (Reading). 2004 Nov;150(Pt 11):3877-3887. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27299-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 15528672
-
Catabolite repression 1985.Biochimie. 1985 Jan;67(1):29-34. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80227-3. Biochimie. 1985. PMID: 2986729 Review.
-
Mutations in the Global Transcription Factor CRP/CAP: Insights from Experimental Evolution and Deep Sequencing.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Jun 18;17:730-736. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.05.009. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31303977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxypropionate) from glycerol using engineered Klebsiella pneumoniae strain without vitamin B12.Bioengineered. 2015;6(2):77-81. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2015.1011027. Bioengineered. 2015. PMID: 25621933 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional insight into the Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein PrpR reveals a novel type of transcription factor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Oct 10;47(18):9934-9949. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz724. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31504787 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Amine Oxidase of Escherichia coli Is a Metabolic Enzyme that Can Use a Human Leukocyte Molecule as a Substrate.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 10;10(11):e0142367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142367. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26556595 Free PMC article.
-
MapMaker and PathTracer for tracking carbon in genome-scale metabolic models.Biotechnol J. 2016 May;11(5):648-61. doi: 10.1002/biot.201500267. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Biotechnol J. 2016. PMID: 26771089 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Global Regulators RpoS and Cyclic-AMP/CRP on the Catabolome and Transcriptome of Escherichia coli K12 during Carbon- and Energy-Limited Growth.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 23;10(7):e0133793. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133793. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26204448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1474. - PubMed
-
- Borgne, S. L., B. Palmeros, F. Valle, F. Bolivar, and G. Gosset. 1998. pBRINT-Ts: a plasmid family with a temperature-sensitive replicon, designed for chromosomal integration into the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. Gene 223:213-219. - PubMed
-
- Busby, S., and R. H. Ebright. 1997. Transcription activation at class II CAP-dependent promoters. Mol. Microbiol. 23:853-859. - PubMed
-
- Busby, S., and R. H. Ebright. 1999. Transcription activation by catabolite activator protein (CAP). J. Mol. Biol. 293:199-213. - PubMed
-
- Cases, I., J. Pérez-Martín, and V. Lorenzo. 1999. The IIANtr (PtsN) protein of Pseudomonas putida mediates the C source inhibition of the σ54-dependent Pu promoter of the TOL plasmid. J. Biol. Chem. 274:15562-15568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

