Regulation of Id2 expression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta
- PMID: 15809228
- PMCID: PMC1074397
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki339
Regulation of Id2 expression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta
Abstract
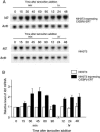
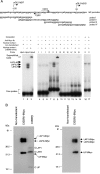
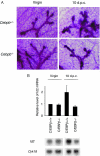
Mice deficient for Id2, a negative regulator of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors, exhibit a defect in lactation due to impaired lobuloalveolar development during pregnancy, similar to the mice lacking the CCAAT enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) beta. Here, we show that Id2 is a direct target of C/EBPbeta. Translocation of C/EBPbeta into the nucleus, which was achieved by using a system utilizing the fusion protein between C/EBPbeta and the ligand-binding domain of the human estrogen receptor (C/EBPbeta-ERT), demonstrated the rapid induction of endogenous Id2 expression. In reporter assays, transactivation of the Id2 promoter by C/EBPbeta was observed and, among three potential C/EBPbeta binding sites found in the 2.3 kb Id2 promoter region, the most proximal element was responsible for the transactivation. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) identified this element as a core sequence to which C/EBPbeta binds. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) furthermore confirmed the presence of C/EBPbeta in the Id2 promoter region. Northern blotting showed that Id2 expression in C/EBPbeta-deficient mammary glands was reduced at 10 days post coitus (d.p.c.), compared with that in wild-type mammary glands. Thus, our data demonstrate that Id2 is a direct target of C/EBPbeta and provide insight into molecular mechanisms underlying mammary gland development during pregnancy.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcriptional cooperation between NF-kappaB p50 and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta regulates Nur77 transcription in Leydig cells.J Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Feb;42(2):131-8. doi: 10.1677/JME-08-0016. Epub 2008 Nov 7. J Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 18996961
-
Role of hepatitis B virus X repression of C/EBPbeta activity in the down-regulation of glutathione S-transferase A2 gene: implications in other phase II detoxifying enzyme expression.Xenobiotica. 2009 Feb;39(2):182-92. doi: 10.1080/00498250802549808. Xenobiotica. 2009. PMID: 19255944
-
Sequential gene promoter interactions by C/EBPbeta, C/EBPalpha, and PPARgamma during adipogenesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 May 21;318(1):213-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.04.017. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15110775
-
In vivo function of a differentiation inhibitor, Id2.IUBMB Life. 2001 Apr;51(4):207-14. doi: 10.1080/152165401753311744. IUBMB Life. 2001. PMID: 11569914 Review.
-
A role for Id proteins in mammary gland physiology and tumorigenesis.Adv Cancer Res. 2004;92:81-94. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(04)92004-0. Adv Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15530557 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitor of binding/differentiation 2 (Id2) is regulated by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (C/EBPα) and promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 1;8(11):2254-2266. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30555742 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic control of natural killer cell maturation by histone H2A deubiquitinase, MYSM1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 8;110(41):E3927-36. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308888110. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24062447 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-specific differences in the mechanisms of progesterone regulation of murine mammary gland development.Endocrinology. 2009 Mar;150(3):1485-94. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1459. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 18988671 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Thermogenesis and a Molecular Signature for Brown Adipose Tissue in Id2 Null Mice.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:6785948. doi: 10.1155/2016/6785948. Epub 2016 Apr 10. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 27144179 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorα agonists differentially regulate inhibitor of DNA binding expression in rodents and human cells.PPAR Res. 2012;2012:483536. doi: 10.1155/2012/483536. Epub 2012 Jun 4. PPAR Res. 2012. PMID: 22701468 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neville M.C., Daniel C.W. The Mammary gland: Development, Regulation, and Function. New York, NY: Plenum Press; 1987.
-
- Hennighausen L., Robinson G.W. Signaling pathways in mammary gland development. Dev. Cell. 2001;1:467–475. - PubMed
-
- Ruzinova M.B., Benezra R. Id proteins in development, cell cycle and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:410–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

