PI(4,5)P2-dependent microdomain assemblies capture microtubules to promote and control leading edge motility
- PMID: 15809307
- PMCID: PMC2171909
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200407058
PI(4,5)P2-dependent microdomain assemblies capture microtubules to promote and control leading edge motility
Abstract
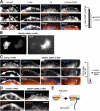
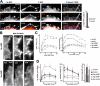
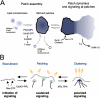
The lipid second messenger PI(4,5)P(2) modulates actin dynamics, and its local accumulation at plasmalemmal microdomains (rafts) might mediate regulation of protrusive motility. However, how PI(4,5)P(2)-rich rafts regulate surface motility is not well understood. Here, we show that upon signals promoting cell surface motility, PI(4,5)P(2) directs the assembly of dynamic raft-rich plasmalemmal patches, which promote and sustain protrusive motility. The accumulation of PI(4,5)P(2) at rafts, together with Cdc42, promotes patch assembly through N-WASP. The patches exhibit locally regulated PI(4,5)P(2) turnover and reduced diffusion-mediated exchange with their environment. Patches capture microtubules (MTs) through patch IQGAP1, to stabilize MTs at the leading edge. Captured MTs in turn deliver PKA to patches to promote patch clustering through further PI(4,5)P(2) accumulation in response to cAMP. Patch clustering restricts, spatially confines, and polarizes protrusive motility. Thus, PI(4,5)P(2)-dependent raft-rich patches enhance local signaling for motility, and their assembly into clusters is regulated through captured MTs and PKA, coupling local regulation of motility to cell polarity, and organization.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spatial control of actin-based motility through plasmalemmal PtdIns(4,5)P2-rich raft assemblies.Biochem Soc Symp. 2005;(72):119-27. doi: 10.1042/bss0720119. Biochem Soc Symp. 2005. PMID: 15649136 Review.
-
Missing-in-metastasis and IRSp53 deform PI(4,5)P2-rich membranes by an inverse BAR domain-like mechanism.J Cell Biol. 2007 Mar 26;176(7):953-64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200609176. Epub 2007 Mar 19. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17371834 Free PMC article.
-
New EMBO members' review: actin cytoskeleton regulation through modulation of PI(4,5)P(2) rafts.EMBO J. 2001 Aug 15;20(16):4332-6. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4332. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11500359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of IQGAP1 in cell polarization and migration.Novartis Found Symp. 2005;269:92-101; discussion 101-5, 223-30. Novartis Found Symp. 2005. PMID: 16355537
-
Calcium-dependent interaction of Lis1 with IQGAP1 and Cdc42 promotes neuronal motility.Nat Neurosci. 2006 Jan;9(1):50-7. doi: 10.1038/nn1619. Epub 2005 Dec 20. Nat Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16369480
Cited by
-
Supervised membrane swimming: small G-protein lifeguards regulate PIPK signalling and monitor intracellular PtdIns(4,5)P2 pools.Biochem J. 2006 Aug 15;398(1):1-13. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060565. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16856876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 23;284(43):29489-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038034. Epub 2009 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19729450 Free PMC article.
-
Local PIP(2) signals: when, where, and how?Pflugers Arch. 2007 Oct;455(1):55-67. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0280-9. Epub 2007 May 30. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17534652 Review.
-
Protein kinase A activity is regulated by actomyosin contractility during cell migration and is required for durotaxis.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Jan 1;31(1):45-58. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-03-0131. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 31721649 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular markers for granulovacuolar degeneration are present in rimmed vacuoles.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 28;8(11):e80995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080995. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cremona, O., and P. De Camilli. 2001. Phosphoinositides in membrane traffic at the synapse. J. Cell Sci. 114:1041–1052. - PubMed
-
- del Pozo, M.A., N.B. Alderson, W.B. Kiosses, H.-H. Chiang, R.G.W. Anderson, and M.A. Schwartz. 2004. Integrins regulate Rac targeting by internalization of membrane domains. Science. 303:839–842. - PubMed
-
- Etienne-Manneville, S., and A. Hall. 2002. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 420:629–635. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

