The subendothelial extracellular matrix modulates NF-kappaB activation by flow: a potential role in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 15809308
- PMCID: PMC2171897
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200410073
The subendothelial extracellular matrix modulates NF-kappaB activation by flow: a potential role in atherosclerosis
Abstract
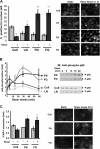
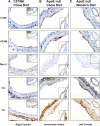
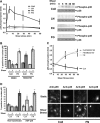
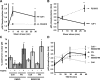
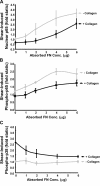
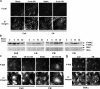
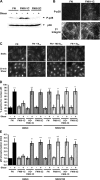
Atherosclerotic plaque forms in regions of the vasculature exposed to disturbed flow. NF-kappaB activation by fluid flow, leading to expression of target genes such as E-selectin, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1, may regulate early monocyte recruitment and fatty streak formation. Flow-induced NF-kappaB activation is downstream of conformational activation of integrins, resulting in new integrin binding to the subendothelial extracellular matrix and signaling. Therefore, we examined the involvement of the extracellular matrix in this process. Whereas endothelial cells plated on fibronectin or fibrinogen activate NF-kappaB in response to flow, cells on collagen or laminin do not. In vivo, fibronectin and fibrinogen are deposited at atherosclerosis-prone sites before other signs of atherosclerosis. Ligation of integrin alpha2beta1 on collagen prevents flow-induced NF-kappaB activation through a p38-dependent pathway that is activated locally at adhesion sites. Furthermore, altering the extracellular matrix to promote p38 activation in cells on fibronectin suppresses NF-kappaB activation, suggesting a novel therapeutic strategy for treating atherosclerosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix-specific suppression of integrin activation in shear stress signaling.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Nov;17(11):4686-97. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-04-0289. Epub 2006 Aug 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16928957 Free PMC article.
-
αvβ3 Integrins Mediate Flow-Induced NF-κB Activation, Proinflammatory Gene Expression, and Early Atherogenic Inflammation.Am J Pathol. 2015 Sep;185(9):2575-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.05.013. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26212910 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix-specific protein kinase A signaling regulates p21-activated kinase activation by flow in endothelial cells.Circ Res. 2010 Apr 30;106(8):1394-403. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.210286. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20224042 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.Am J Cardiol. 1995 Sep 28;76(9):18C-23C. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)80466-4. Am J Cardiol. 1995. PMID: 7572682 Review.
-
Inflammation meets oxidation: NF-kappaB as a mediator of initial lesion development in atherosclerosis.Trends Mol Med. 2003 Dec;9(12):549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2003.10.007. Trends Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 14659470 Review.
Cited by
-
The atypical structure and function of newborn arterial endothelium is mediated by Rho/Rho kinase signaling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Aug 15;307(4):H628-32. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00327.2014. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24951756 Free PMC article.
-
De novo designed transmembrane peptides activating the α5β1 integrin.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2018 May 1;31(5):181-190. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzy014. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2018. PMID: 29992271 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Screening of Vascular Endothelium-Destructive or Protective Microenvironments: Cooperative Actions of Extracellular Matrix Composition, Stiffness, and Structure.Adv Healthc Mater. 2017 Jun;6(11):10.1002/adhm.201601426. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601426. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. PMID: 28337850 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbed flow-induced Gs-mediated signaling protects against endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis.JCI Insight. 2020 Dec 3;5(23):e140485. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.140485. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 33268595 Free PMC article.
-
Matricryptic sites control tissue injury responses in the cardiovascular system: relationships to pattern recognition receptor regulated events.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Mar;48(3):454-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.09.002. Epub 2009 Sep 12. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 19751741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alpert, D., P. Schwenger, J. Han, and J. Vilcek. 1999. Cell stress and MKK6b-mediated p38 MAP kinase activation inhibit tumor necrosis factor-induced IkappaB phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274:22176–22183. - PubMed
-
- Belkin, A.M., and M.A. Stepp. 2000. Integrins as receptors for laminins. Microsc. Res. Tech. 51:280–301. - PubMed
-
- Bhullar, I.S., Y.S. Li, H. Miao, E. Zandi, M. Kim, J.Y. Shyy, and S. Chien. 1998. Fluid shear stress activation of IkappaB kinase is integrin-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 273:30544–30549. - PubMed
-
- Bowie, A.G., and L.A. O'Neill. 2000. Vitamin C inhibits NF-kappa B activation by TNF via the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Immunol. 165:7180–7188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

