Hierarchy of resistance to cervical neoplasia mediated by combinations of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor and human leukocyte antigen loci
- PMID: 15809352
- PMCID: PMC2213116
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20042158
Hierarchy of resistance to cervical neoplasia mediated by combinations of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor and human leukocyte antigen loci
Abstract
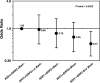
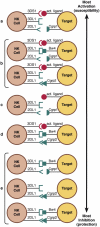
Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) recognition of specific human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I allotypes contributes to the array of receptor-ligand interactions that determine natural killer (NK) cell response to its target. Contrasting genetic effects of KIR/HLA combinations have been observed in infectious and autoimmune diseases, where genotypes associated with NK cell activation seem to be protective or to confer susceptibility, respectively. We show here that combinations of KIR and HLA loci also affect the risk of developing cervical neoplasia. Specific inhibitory KIR/HLA ligand pairs decrease the risk of developing neoplasia, whereas the presence of the activating receptor KIR3DS1 results in increased risk of disease, particularly when the protective inhibitory combinations are missing. These data suggest a continuum of resistance conferred by NK cell inhibition to susceptibility involving NK cell activation in the development of cervical neoplasia and underscore the pervasive influence of KIR/HLA genetic variation in human disease pathogenesis.
Figures

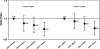
References
-
- Lodoen, M.B., and L.L. Lanier. 2005. Viral modulation of NK cell immunity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:59–69. - PubMed
-
- Biron, C.A., and L. Brossay. 2001. NK cells and NKT cells in innate defense against viral infections. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13:458–464. - PubMed
-
- Long, E.O., and S. Rajagopalan. 2000. HLA class I recognition by killer cell Ig-like receptors. Semin. Immunol. 12:101–108. - PubMed
-
- Vales-Gomez, M., H. Reyburn, and J. Strominger. 2000. Interaction between the human NK receptors and their ligands. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 20:223–244. - PubMed
-
- Vivier, E., J.A. Nunes, and F. Vely. 2004. Natural killer cell signaling pathways. Science. 306:1517–1519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

