VEGF-A induces tumor and sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and promotes lymphatic metastasis
- PMID: 15809353
- PMCID: PMC2213132
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041896
VEGF-A induces tumor and sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and promotes lymphatic metastasis
Abstract
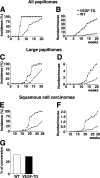
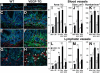
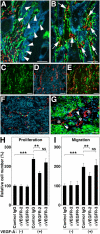
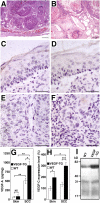
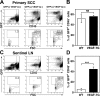
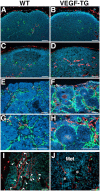
The mechanisms of tumor metastasis to the sentinel lymph nodes are poorly understood. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A plays a principle role in tumor progression and angiogenesis; however, its role in tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis has remained unclear. We created transgenic mice that overexpress VEGF-A and green fluorescent protein specifically in the skin, and subjected them to a standard chemically-induced skin carcinogenesis regimen. We found that VEGF-A not only strongly promotes multistep skin carcinogenesis, but also induces active proliferation of VEGF receptor-2-expressing tumor-associated lymphatic vessels as well as tumor metastasis to the sentinel and distant lymph nodes. The lymphangiogenic activity of VEGF-A-expressing tumor cells was maintained within metastasis-containing lymph nodes. The most surprising finding of our study was that even before metastasizing, VEGF-A-overexpressing primary tumors induced sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis. This suggests that primary tumors might begin preparing their future metastatic site by producing lymphangiogenic factors that mediate their efficient transport to sentinel lymph nodes. This newly identified mechanism of inducing lymph node lymphangiogenesis likely contributes to tumor metastasis, and therefore, represents a new therapeutic target for advanced cancer and/or for the prevention of metastasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elevated VEGF-D Modulates Tumor Inflammation and Reduces the Growth of Carcinogen-Induced Skin Tumors.Neoplasia. 2016 Jul;18(7):436-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2016.05.002. Neoplasia. 2016. PMID: 27435926 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis in sentinel lymph nodes promotes tumor metastasis to distant sites.Blood. 2007 Feb 1;109(3):1010-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-021758. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17032920 Free PMC article.
-
p19/Arf and p53 suppress sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and carcinoma metastasis.Oncogene. 2008 May 15;27(22):3145-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210973. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18059331
-
Tumor lymphangiogenesis and melanoma metastasis.J Cell Physiol. 2008 Aug;216(2):347-54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21494. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18481261 Review.
-
Tumor and lymph node lymphangiogenesis--impact on cancer metastasis.J Leukoc Biol. 2006 Oct;80(4):691-6. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1105653. Epub 2006 Jun 22. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16793912 Review.
Cited by
-
Reprogramming of sentinel lymph node microenvironment during tumor metastasis.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Oct 20;29(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00868-1. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36266717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in breast cancer tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis.Lymphat Res Biol. 2012 Sep;10(3):97-106. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2012.0010. Lymphat Res Biol. 2012. PMID: 22984905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of a novel highly metastatic melanoma cell line identifies osteopontin as a new lymphangiogenic factor.Int J Oncol. 2012 Oct;41(4):1455-63. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1548. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22797548 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatics in Tumor Progression and Immunomodulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 15;23(4):2127. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042127. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of the meningeal lymphatic vessels in aging and central nervous system disorders.Cell Biosci. 2022 Dec 17;12(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00942-z. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36528776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Folkman, J. 1992. The role of angiogenesis in tumor growth. Semin. Cancer Biol. 3:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara, N., H.P. Gerber, and J. LeCouter. 2003. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 9:669–676. - PubMed
-
- Skobe, M., T. Hawighorst, D.G. Jackson, R. Prevo, L. Janes, P. Velasco, L. Riccardi, K. Alitalo, K. Claffey, and M. Detmar. 2001. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 7:192–198. - PubMed
-
- Stacker, S.A., C. Caesar, M.E. Baldwin, G.E. Thornton, R.A. Williams, R. Prevo, D.G. Jackson, S. Nishikawa, H. Kubo, and M.G. Achen. 2001. VEGF-D promotes the metastatic spread of tumor cells via the lymphatics. Nat. Med. 7:186–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

