Cholinergic stimulation blocks endothelial cell activation and leukocyte recruitment during inflammation
- PMID: 15809354
- PMCID: PMC2213139
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040463
Cholinergic stimulation blocks endothelial cell activation and leukocyte recruitment during inflammation
Abstract
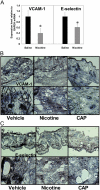
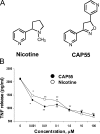
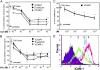
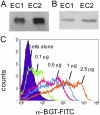
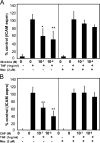
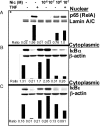
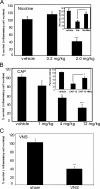
Endothelial cell activation plays a critical role in regulating leukocyte recruitment during inflammation and infection. Based on recent studies showing that acetylcholine and other cholinergic mediators suppress the production of proinflammatory cytokines via the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (alpha7 nAChR) expressed by macrophages and our observations that human microvascular endothelial cells express the alpha7 nAChR, we examined the effect of cholinergic stimulation on endothelial cell activation in vitro and in vivo. Using the Shwartzman reaction, we observed that nicotine (2 mg/kg) and the novel cholinergic agent CAP55 (12 mg/kg) inhibit endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression. Using endothelial cell cultures, we observed the direct inhibitory effects of acetylcholine and cholinergic agents on tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced endothelial cell activation. Mecamylamine, an nAChR antagonist, reversed the inhibition of endothelial cell activation by both cholinergic agonists, confirming the antiinflammatory role of the nAChR cholinergic pathway. In vitro mechanistic studies revealed that nicotine blocked TNF-induced nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear entry in an inhibitor kappaB (IkappaB)alpha- and IkappaBepsilon-dependent manner. Finally, with the carrageenan air pouch model, both vagus nerve stimulation and cholinergic agonists significantly blocked leukocyte migration in vivo. These findings identify the endothelium, a key regulator of leukocyte trafficking during inflammation, as a target of anti-inflammatory cholinergic mediators.
Figures


References
-
- Cines, D.B., E.S. Pollak, C.A. Buck, J. Loscalzo, G.A. Zimmerman, R.P. McEver, J.S. Pober, T.M. Wick, B.A. Konkle, B.S. Schwartz, et al. 1998. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 91:3527–3561. - PubMed
-
- Cronstein, B.N., S.C. Kimmel, R.I. Levin, F. Martiniuk, and G. Weissmann. 1992. A mechanism for the antiinflammatory effects of corticosteroids: the glucocorticoid receptor regulates leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and expression of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 and intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.. 89:9991–9995. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tracey, K.J. 2002. The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 420:853–859. - PubMed
-
- Borovikova, L.V., S. Ivanova, M. Zhang, H. Yang, G.I. Botchkina, L.R. Watkins, H. Wang, N. Abumrad, J.W. Eaton, and K.J. Tracey. 2000. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature. 405:458–462. - PubMed
-
- Wang, H., M. Yu, M. Ochani, C.A. Amella, M. Tanovic, S. Susarla, J.H. Li, H. Yang, L. Ulloa, Y. Al-Abed, et al. 2003. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature. 421:384–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

