Dynamics of Z-band based proteins in developing skeletal muscle cells
- PMID: 15810059
- PMCID: PMC1993831
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20063
Dynamics of Z-band based proteins in developing skeletal muscle cells
Abstract
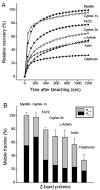
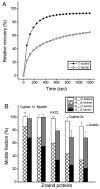
During myofibril formation, Z-bodies, small complexes of alpha-actinin and associated proteins, grow in size, fuse and align to produce Z-bands. To determine if there were changes in protein dynamics during the assembly process, Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching was used to measure the exchange of Z-body and Z-band proteins with cytoplasmic pools in cultures of quail myotubes. Myotubes were transfected with plasmids encoding Yellow, Green, or Cyan Fluorescent Protein linked to the Z-band proteins: actin, alpha-actinin, cypher, FATZ, myotilin, and telethonin. Each Z-band protein showed a characteristic recovery rate and mobility. All except telethonin were localized in both Z-bodies and Z-bands. Proteins that were present both early in development in Z-bodies and later in Z-bands had faster exchange rates in Z-bodies. These results suggest that during myofibrillogenesis, molecular interactions develop between the Z-band proteins that decrease their mobility and increase the stability of the Z-bands. A truncated construct of alpha-actinin, which localized in Z-bands in myotubes and exhibited a very low rate of exchange, led to disruption of myofibrils, suggesting the importance of dynamic, intact alpha-actinin molecules for the formation and maintenance of Z-bands. Our experiments reveal the Z-band to be a much more dynamic structure than its appearance in electron micrographs of cross-striated muscle cells might suggest.
Figures
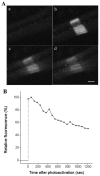
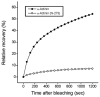
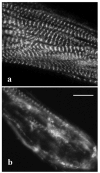
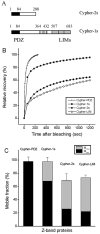

References
-
- Ayoob JC, Turnacioglu KK, Mittal B, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Targeting of cardiac muscle titin fragments to the Z-bands and dense bodies of living muscle and non-muscle cells. Cell Motil Cyotskel. 2000;45:67–82. - PubMed
-
- Ayoob JC, Shaner NC, Sanger JW, Sanger JM. Expression of green or red fluorescent protein (GFP or DsRed) linked proteins in nonmuscle and muscle cells. Mol Biotechnology. 2001;17:65–71. - PubMed
-
- Bandman E. Myosin isoenzyme transitions in muscle development, maturation and disease. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;97:97–131. - PubMed
-
- Bastiaens PIH, Pepperkok R. Observing proteins in their natural habitat: the living cell. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:631–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

