Loss of heterozygosity in multistage carcinogenesis of esophageal carcinoma at high-incidence area in Henan Province, China
- PMID: 15810068
- PMCID: PMC4305771
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2055
Loss of heterozygosity in multistage carcinogenesis of esophageal carcinoma at high-incidence area in Henan Province, China
Abstract
Aim: Microsatellites are the repeated DNA sequences scattered widely within the genomes and closely linked with many important genes. This study was designed to characterize the changes of microsatellite DNA loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in esophageal carcinogenesis.
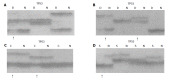
Methods: Allelic deletions in 32 cases of matched precancerous, cancerous and normal tissues were examined by syringe microdissection under an anatomic microscope and microsatellite polymorphism analysis using 15 polymorphic markers on chromosomes 3p, 5q, 6p, 9p, 13q, 17p, 17q and 18q.
Results: Microsatellite DNA LOH was observed in precancerous and cancerous tissues, except D9S1752. The rate of LOH increased remarkably with the lesions progressed from basal cell hyperplasia (BCH) to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) (P<0.05). Three markers, D9S171, D13S260 and TP53, showed the highest incidence of LOH (>60%). LOH loci were different in precancerous and cancerous tissues. LOH in D3S1234 and TP53 was the common event in different lesions from the same patients.
Conclusion: Microsatellite DNA LOH occurs in early stage of human esophageal carcinogenesis, even in BCH. With the lesion progressed, gene instability increases, the accumulation of this change may be one of the important mechanisms driving precancerous lesions to cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Wang LD, Zheng S. The mechanism of esophageal and gastric cardia carcinogenesis from the subjects at high-incidence area for esophageal cancer in Henan. Zhengzhou Daxue Xuebao. 2002;37:717–729.
-
- Cullis CA. The use of DNA polymorphisms in genetic mapping. Genet Eng (N Y) 2002;24:179–189. - PubMed
-
- Wang LD, Shi ST, Zhou Q, Goldstein S, Hong JY, Shao P, Qiu SL, Yang CS. Changes in p53 and cyclin D1 protein levels and cell proliferation in different stages of human esophageal and gastric-cardia carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer. 1994;59:514–519. - PubMed
-
- Wang LD, Zhou Q, Hong JY, Qiu SL, Yang CS. p53 protein accumulation and gene mutations in multifocal esophageal precancerous lesions from symptom free subjects in a high incidence area for esophageal carcinoma in Henan, China. Cancer. 1996;77:1244–1249. - PubMed
-
- Wang LD, Hong JY, Qiu SL, Gao H, Yang CS. Accumulation of p53 protein in human esophageal precancerous lesions: a possible early biomarker for carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993;53:1783–1787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

